Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
population is increasing rapidly, distributed between very poor regions
with low consumption of natural resources and rich regions that
depend heavily on fossil fuels. The inequalities are less accentuated in
scenario SSP4, called “inequality”. Scenario SSP2, called “middle of
the road”, prolongs the tendencies of the last decades and corresponds
to the intermediary assumptions. Finally, scenario SSP5 corresponds
to an increased consumption of fossil fuels and a weak awareness of
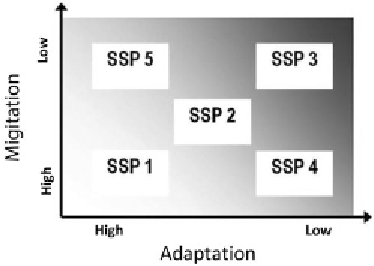
environmental questions. Figure 4.1 presents different levels of
engagement on mitigation and adaptation associated with the SSP
scenarios. At the extremes are scenarios SSP1 and SSP3 with the
greatest and smallest levels of engagement on mitigation and
adaptation to climate change.
Figure 4.1.
Different levels of engagement associated with the SSP scenarios
4.3.2.
Impacts of climate change on coastal zones on different time
scales
The changes resulting from the increase in concentrations of
greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, their effects on different time
scales on the different subsystems of the climate system and their
impacts on the coastal zones will now be addressed. First, we will
analyze the climate factors that have short-term impacts on the
seashore. For example, the passage of a storm through the coast with a
duration, normally, of less than a week, leads to a temporary elevation


Search WWH ::

Custom Search