Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
14.10 Fill slopes
•
The strength of underlying materials often dictates the slope stability.
Table 14.10
Typical batters of fill slopes (Hoerner, 1990).
Material
Slope batters (Vertical : Horizontal)
Hard rock fill
1V: 1.5H to 1V: 1H
Weak rock fill
1V: 2H to 1V: 1.25H
Gravel
1V: 2H to 1V: 1.25H
Sand
1V: 2.5H to 1V: 1.5H
Clay
1V: 4H to 1V: 1.5H
•
Table assumes no surcharge at the top.
•
A guide only. Depends on risk acceptable, surcharge, water table and ground
underlying embankment. Slope stability analysis required.
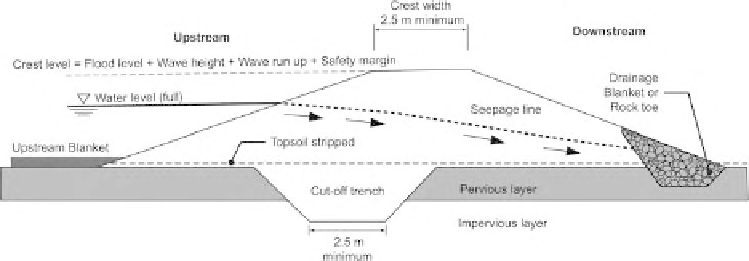
Figure 14.2
Typical small earth dam.
14.11 Factors of safety for dam walls
•
Dam walls can typically have complex geometry with cores and outer zones.
Table 14.11
Factors of safety for dam walls.
Seepage condition
Storage
Required factor
Design consideration
of safety
Steady seepage
With maximum storage pool
1.5
Long term condition
Sudden drawdown
From maximum pool
1.1
Short term condition
From spillway crest
1.3
End of construction
Reservoir empty
1.3
Short term condition
Earthquake
With maximum storage pool
1.1
Pseudo-static approach.
Long term condition






Search WWH ::

Custom Search