Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
7.5 Data Delivery and Project Operationalization
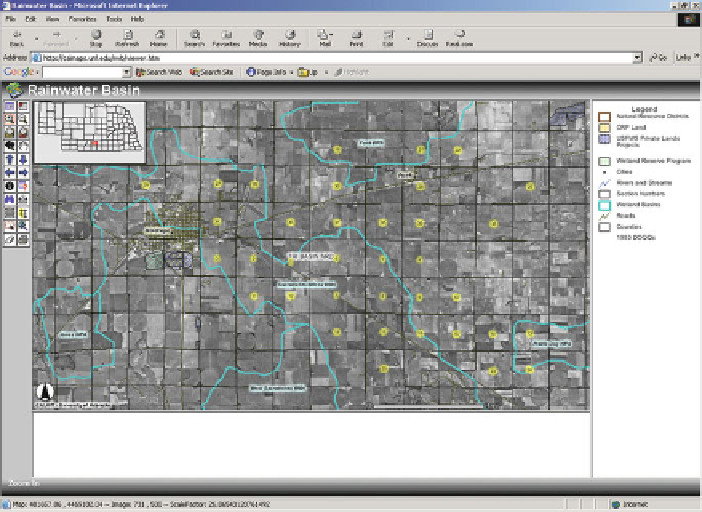
All geospatial data, including imagery, RUSLE modeling results, metadata and doc-
umentation were made available to RWBJV partners and staff via a Rainwater Basin
GIS Internet site (
http://www.calmit.unl.edu/rwb
/). This site was designed to facil-
itate both data download, for those who had GIS software available and mapping
functions that require users to have no additional software to visualize datasets
(Fig.
7.4
).
In the years since the initial project was completed, the RWBJV has made sub-
stantial progress in adopting and using both GIS and remote sensing technologies.
An initial development was the establishment of a RWBJV GIS Steering Committee
to foster enhancement of datasets, use of GIS for modeling and decision support,
and interagency collaboration in seeking financial support through grants (Smith
and Lucas
1998
). One result of this collaboration has been a multiyear program to
acquire 2-foot resolution color infrared aerial photography during spring to docu-
ment the extent of wetlands and wetlands use by waterfowl. Recently, this program
has been augmented by a cooperative project to acquire LiDAR data over the
RWB. These data will be used to develop high resolution digital elevation models
(2-foot contours) important for identifying hydrologic modifications such as surface
drains and ditches and to better delineate wetland basins in this region of low relief
(Merrick and Company
2009
).
Fig. 7.4
All geospatial data, including imagery, RUSLE modeling results, metadata and doc-
umentation were made available to RWBJV partners and staff via the Internet (
http://www.
calmit.unl.edu/rwb
/)