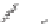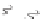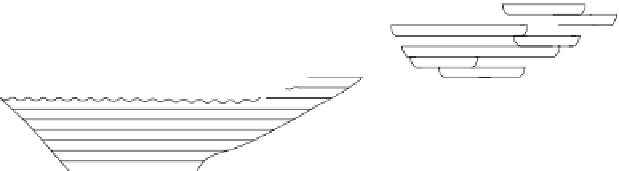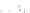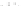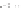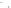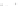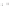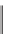Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
MFS
high
TS
SB
relative
sea-level
low
t
0
t
2
t
4
t
6
t
8
t
10
t
12
t
14
t
16
t
18
t
20
t
22
t
24
t
26
t
28
t
29
(a)
time
SHELF BREAK MARGIN
p
d
(
t
29
sea-level
(b)
time representing
condensation due to
associated with the MFS
t
28
marine hiatus or
sediment starvation
t
26
t
24
MFS
TS
t
22
t
20
t
18
time representing non-marine erosion
and non-deposition associated with
formation of the SB
t
16
t
14
t
12
t
10
t
8
eroded strata
SB
t
6
correlative conformity
t
4
t
2
t
0
(c)
distance along depositional profile
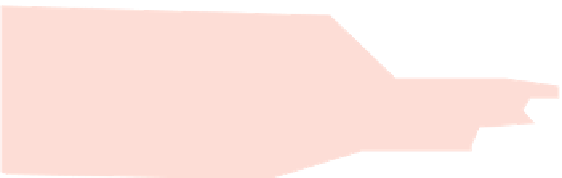
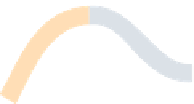
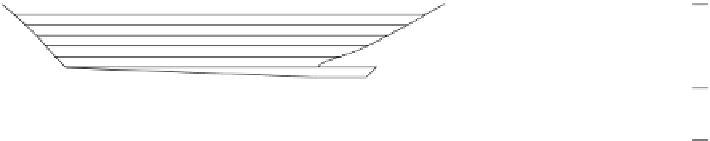
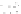
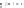
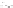
Figure A6.15
Sequence stratigraphy summary fi gures. (a) Idealized illustrations of key features of the
sequence stratigraphy model on the relative sea-level curve for (b) to (e), showing the position of the systems
tracts and key surfaces. In this example, parasequences are assumed to have equal duration as indicated by the
equal time units
t
0
,
t
2
, etc. (b and d) Cross-sections through a HST and the overlying depositional sequence
(FSST, LST, TST and HST) for a continental margin with a shelf break (b) and ramp type continental margin (d).
(c and e) Chronostratigraphical representation of (b) and (d) respectively. Hemipelagic and pelagic sediments
are not shown. (From Coe 2003.)