Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Distinguishing between micrite and sparite
Micrite and sparite are both forms of calcite, the only physical
difference between them being the grain or crystal size. Micrite
refers to calcite that is less than 4 µm (0.004 mm) in size and
sparite refers to calcite that is greater than 4 µm (0.004 mm) in
size. They can be distinguished in hand specimen; sparite is
translucent or semi-translucent because the large crystal size
transmits the light through it, whereas micrite is opaque
because of its small grain size. Micrite is often white or cream
but it can also have pink, yellow or even green tinges
depending on the other minerals present. You may fi nd it
useful to wet the rock specimen before you look at it through a
hand lens to distinguish micrite from sparite.
The distinction between micrite and sparite is important
because it yields information about the depositional process.
Micrite is precipitated and settles out from suspension at the
time of deposition as a matrix, and indicates low energy
conditions. In contrast, sparite is a cement which is
precipitated after deposition. Sparite can be subdivided into
several different types; including poikilotopic (large crystals
enclosing several grains); drusy (small- to medium-sized
crystals which increase in size away from the edge of the grains
into the centre of the cavity); isopachous (a thin fringe around
the grains); and syntaxial overgrowth (crystal in optical
continuity with the grain it has overgrown).
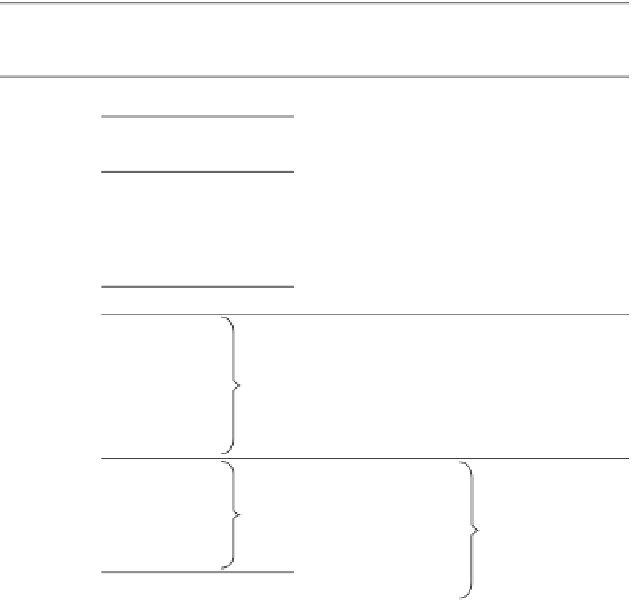
sediment and sedimentary
rock terms implying grain size
mm
grain term
boulders
256
128
64
32
16
8
4
2
1
0.5
0.25
0.125
0.062
0.031
0.016
0.008
0.004
cobbles
gravel, rudite,
rudaceous sediments,
conglomerates, breccias
pebbles
granules
very coarse
coarse
medium
fine
very fine
coarse
medium
fine
very fine
clay
sand, sandstone, arenites,
arenaceous sediments
sand
silt, siltstone
silt
mud,
mudrocks
Figure A6.1
Grain-size
descriptors.
clay, claystone