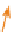Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Second, oceanographers have always believed that
about one-third of fossil fuel emissions enters the ocean
each year.
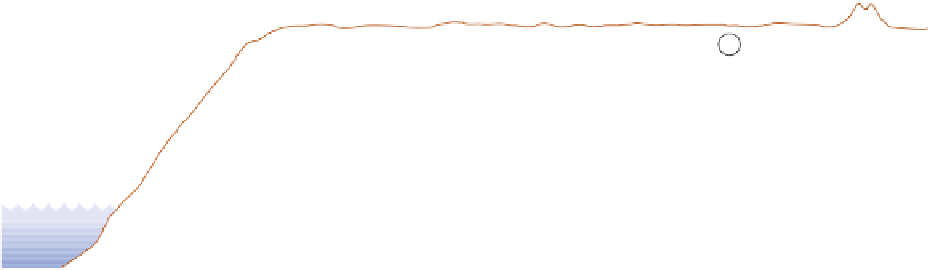
Figure 21.5
shows an annual uptake by the
oceans of 92 C(Pg) that is slightly greater than the return
of 90 C(Pg) to the atmosphere.
Henry's law
states:
of surface and deep waters, not by the dissolution of CO
2
across the surface.
S = kP
Nitrogen (N) is the plant nutrient needed in largest
quantities after carbon, oxygen and hydrogen, and forms
an essential part of the structure of plant proteins. Its cycle
is complex, involving atmosphere, soil and organic
material, and depends upon the activities of a range of
specialized micro-organisms. The main features of the
cycle are shown in
Figure 21.7
.
Organic materials are added to the soil surface upon
the death of a plant or its organs. Waste products are also
added which contain significant quantities of nitrogen.
where S = solubility of a gas in a liquid, k = the solubility
constant, and P = overlying pressure of the atmosphere.
Under one atmosphere of partial pressure, the solubility
of CO
2
is 1.4 at 25
C. Thus excess CO
2
dissolves in sea
water, where it is buffered by the dissolution of marine
carbonates. Because of the low levels of nutrients in sea
water, changes in marine NPP are thought to be
unimportant to the oceanic uptake of anthropogenic CO
2
.
The uptake of CO
2
by the oceans is limited by the mixing
NH
4
+
ELECTRICAL
DISCHARGE
INDUSTRIAL
COMBUSTION
N+O
2
=NO
2
ANIMAL
RAIN
FERTILIZER
7
EXCRETA
N
2
NH
3
MANURE
N
2
NH
4
+
+ NO
3
-
3
6
VOLCANIC
ACTIVITY
MICROBIAL
ACTION
4
5
AQUATIC
SYSTEMS
NH
3
HUMIC
RESIDUES
2
1
DRAINAGE
NO
3
-
NO
2
-
NH
4
+
6
MARINE
CYCLES
EXCHANGEABLE
NH
4
+
FIXED
NH
4
+
2NH
4
+
+ 3O
2
2NO
2
-
+ 4H
+
+ 2H
2
O
1. Nitrosomonas, Nitrosococcus (aerobic)
NITRIFICATION
2NO
2
-
+ O
2
2NO
3
-
2. Nitrobacter (aerobic)
3. Azotobacter (aerobic), Clostridium (anaerobic)
4. Rhizobium (symbiotic)
5. Many bacteria and other organisms
NITROGEN FIXATION
AMMONIFICATION
6. Pseudomonas, Micrococcus, Thiobacillus, Achromobacter
(facultative anaerobes)
DENITRIFICATION
7. Nitrogen salts in rain water, sea spray, bird guano etc.