Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Acidic variants have partially decomposed litter (F
and/or H horizon) at the surface with a thin eluvial Ea or
Ae to give a F-H-Ae-Bw-C-R sequence of horizons. On
basic igneous rocks and calcareous sedimentary rocks the
soils have a strongly formed structure, a relatively high
percentage base saturation and a high cation exchange
capacity, due to expanding clay minerals vermiculite and
montmorillonite (
Plate 18.5
).
A variant has formed on
the ultrabasic rock serpentine in Scotland and on the
Lizard peninsula in England in which magnesium is the
dominant exchangeable cation, often exceeding calcium
by a factor of five. The content of heavy metals such as
nickel, chromium and cobalt is exceptionally high, and
pastures on these soils give heavy-metal poisoning in
cattle, so-called 'staggers'.
The removal of free calcium carbonate from soils by
leaching is called
decalcification
and leads to a lowering
of soil pH. In humid regions free calcium salts will be
partially washed out of the soil profile, but will maintain
pH values above what is typical for the climate (
Plate
bases will be washed downwards during rainfall, but will
be redeposited by upward capilliary movement in dry
periods. This accumulation is called
calcification
and
occurs with calcium carbonate (CaCO
3
) and calcium
sulphate (gypsum, CaSO
4
.2H
2
O), forming calcic (Bk and
Ck) and gypsic (By and Cy) horizons. As gypsum is more
soluble than lime, the gypsic horizon is found below the
calcic horizon (
Plate 18.7
).
It also disappears first from
the soil profile in a sequence of soils from arid to humid
regions. The sequence in
Figure 18.7
shows these changes
taking place along a north-south transect in central
Canada as one moves from a humid to a semi-arid climate
(
Plate 18.8
).
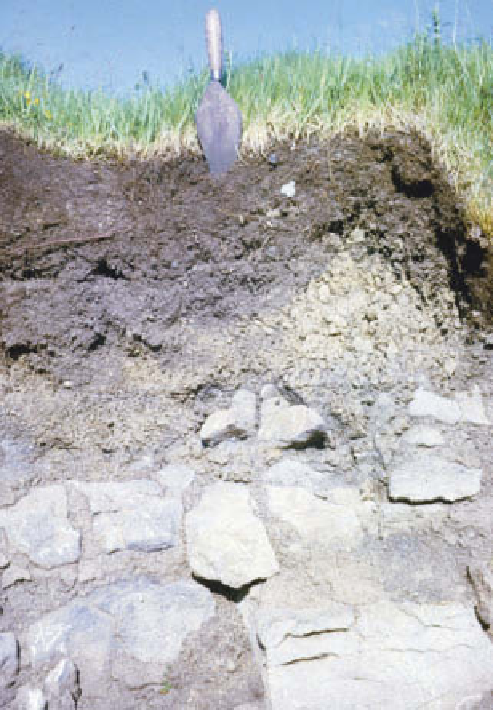
fragments and clay in this Brown Calcareous Soil (FAO: Typic
Calcisol) on Carboniferous Limestone in Upper Wharfedale,
Yorkshire. Ah-Bkw-Rk horizon sequence.
Photo: Ken Atkinson
weathered, basic igneous gabbro, in the Cabrach upland of
Aberdeenshire, Scotland. Scale is in cm.
Photo: Ken Atkinson