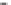Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
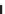
Axis of
deformation
Upstream (m)
Downstream (m)
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
Aggradation,
Frequent channel shifts
Degradation,
Terrace formation
Aggradation,
Strongly braided pattern
Degradation,
Bar destruction
Aggradation,
Strongly braided pattern
Flooded
Degradation
Flooded, Indistinct channel,
Sediment deposition
Sinuosity increase, Bank erosion,
Point-bar growth
Sinuosity increase, Bank erosion,
Point-bar growth
Flooded, Indistinct channel,
Sediment deposition
Figure 14.29
Response of experimental braided and meandering channels to uplift and subsidence across the channel.
Source: After Ouchi (1985)
120
100
80
60
40
20
120
100
80
60
40
UPPER GRAVEL TRAIN
HAREFIELD
WINTER HILL
a
THAMES VALLEY
SUMMERTOWN-RADLEY
20
0
0
LONDON BRIDGE
SWANSCOMBE
SOUTHEND
CLACTON
BANBURY
OXFORD
GORING GAP
READING
SLOUGH
b
SEVERN VALLEY
c
TRENT VALLEY
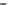
100
100
80
80
60
60
40
40
EAGLE GRAVELS
20
20
0
0
R
RUGELEY
BURTON
NOTTINGHAM
NEWARK
GAINSBOROUGH
HUMBER
SHREWSBURY
IRONBRIDGE
BEWDLEY
WORCESTER
GLOUCESTER
d
UPPER THAMES STRATIGRAPHY
m
KEY
25
ANGLIAN (COLD)
IPSWICHIAN (TEMP)
DEVENSIAN (COLD) TERRACES
HOXNIAN (TEMP)
WOLSTONIAN (COLD)
CONTEMPORARY GLACIAL OUTWASH
Hanborough T.
20
Wolvercote T.
15
Summertown -
Radley T.
10
5
Cold
Temperate
Figure 14.30
Terraces of the rivers (a) Thames, (b) Severn and (c) Trent and their attribution to cold (glacial) or temperate
(interglacial) stages; (d) stratigraphic complexity in the upper Thames around Oxford, where cold-stage terraces overlie or are
incised by temperate-stage channels. (Height in metres above modern flood plain.)
Source: Boulton (1992)