Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
anything like steady rainfall. One of the most common
situations in which this occurs is where moist air is forced
to rise over a mountain barrier. If the moist air is blowing
from the sea at a constant speed, the air will be fairly
uniform and the conversion of vapour to water droplets
will proceed at a constant rate. Rainfall then is often
prolonged and steady.
The short-term variability of rainfall differs greatly
from one area to another. It tends to be greatest in the
tropics; at Djakarta (Indonesia), for example, the annual
rainfall of 1,800 mm falls in only 360 hours on average.
By contrast, the average rainfall in London is only 600
mm, yet it falls in about 500 hours. Variability in precip-
itation is often most important, however, in the more arid
parts of the world, for there even quite small storms may
for months or even years may fill with water, and the baked
clay (adobe) used to make houses may crumble and be
washed away. Within a matter of hours the rainfall may
have ceased and the water almost vanished; within weeks
the vegetation will have died down again.
Singapore
(10m)
Mean annual precipitation = 2282 mm
300
200
100
0
JFMAMJJASOND
equatorial trough zone.
Seasonal variability
In many climates there is a predictable and consistent cycle
of rainfall during the course of the year related to the
latitudinal migration of the wind and pressure systems.
Precipitation areas associated with areas of convergence
and uplift tend to shift polewards in summer and
equatorwards in winter. Some areas, like the British
Isles, remain within the same pressure system throughout
the year and so seasonal variations are subdued. This
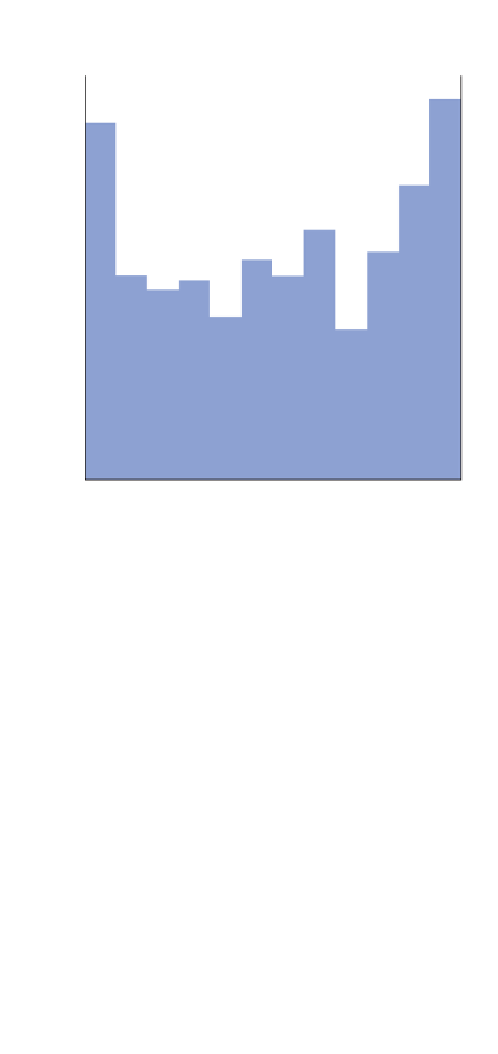
is also true in the equatorial trough zone, where rainfall
can occur at any time throughout the year (
Figure 5.6
),
and in deserts, where rainfall is almost negligible. The
brief, rare storms which do occur can come at any time,
so monthly rainfall, averaged over the long term,
shows little variation (
Figure 5.7
).
Even within the same
pressure belt some seasonal pattern may be evident. In the
Las Vegas (Nevada)
(660m)
Mean annual precipitation = 100 mm
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
JFMAMJJASOND
Nevada, in an arid zone.
Incidence
No.
%
Days with no rain
8634
98·5
Days with rain
78
0·9
Days with a trace of rain
35
0·4
Missing data
19
0·2
Amount (mm)
Under 1
1·1-2·0
2·1-3·0
3·1-5·0
5·1-8·0
8·1-15
Over 15
No. of days in 24 years
27
15
5
14
6
5
6
% of all days
0·31
0·17
0·06
0·16
0·07
0·06
0·07
% of rain days
35
19
6
18
8
6
8