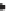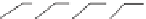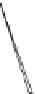Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
The main reason for these differences in gauge height
is snow. We have already mentioned that snowfall is
difficult to measure because of its lightness and tendency
to drift. In the United States the same gauge is used to
measure both snowfall and rain, so it has to be well above
the level of drifting snow. In Canada separate gauges are
used, while in Britain snowfall is a relatively small
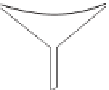
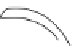
component of the annual precipitation. Shields are often
provided around gauges to reduce the impact of wind, as
seen in
Figure 5.4
.
In normal operation the amount of rainfall collected
in a gauge is measured once a day. In the United States an
appropriately calibrated stick is used to measure the depth
of water which has accumulated in the gauge to obtain the
quantity of rainfall. In Canada and the United Kingdom
the rainwater or melted snow in the gauge is poured into
a glass measuring cylinder, where the rainfall equivalent
Measurement of precipitation
Rain and snow
It is easy to measure rain. Any watertight container sited
well away from buildings and trees will act as a rain gauge.
How much it collects will depend not only upon the
amount of rain and the strength of the wind, but also on
the gauge diameter and its height above the ground.
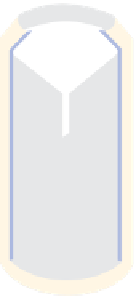
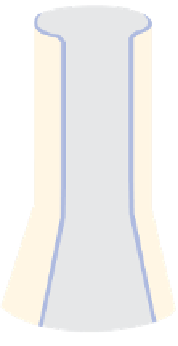
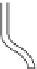
Because of this, rain gauges in the United Kingdom have
a standard diameter of 12·7 cm and are set a fixed distance
of 30 cm above the ground. Unfortunately the standard
varies from country to country, so that in Canada the
diameter is 9 cm at a height of 30 cm above the ground,
while in the United States the gauges are 20 cm wide and
78 cm high (
Figure 5.4
).
Comparisons of rainfall totals
between countries are therefore more difficult than might
be expected.
Tipping bucket
rain gauge
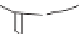
British standard
rain gauge
US Weather Bureau
standard rain gauge
USSR Tretyakov
precipitation gauge
Ground level
rain gauge