Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
Age (Ma)
10
0
10
0
7.0
7.2
20
8.15
7.4
7.6
8.0
8.0
40
7.8
60
80
7.9
100
(b)
Age (Ma)
100
80
60
40
20
0
20
40
60
80
100
0
4.5
20
3.7
4.3
40
4.7
3.9
4.7
3.5
60
4.3
4.1
4.5
80
100
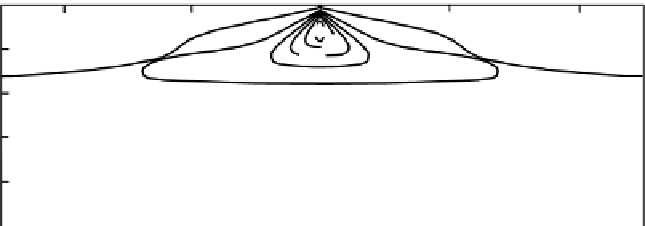
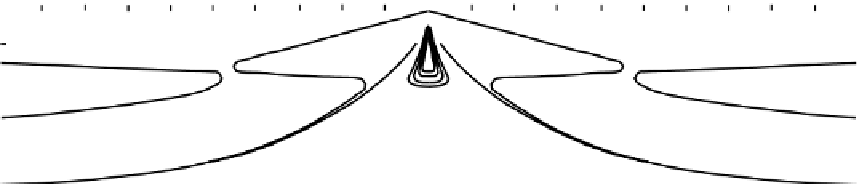
Figure 9.12.
Seismic-velocity models of mid-ocean ridges calculated from a thermal
model similar to those in Section 7.5.2 and theoretical estimates of the dependence
of seismic velocity on temperature and melting of mantle material (assumed to be
peridotite with 0.1% water). (a) Contours of constant P-wave velocity in the oceanic
lithosphere and asthensphere. The 5-Ma-wide, 30-km-deep low-velocity region
centred on the ridge axis is modelled as a zone of extensive melting. (After Solomon
and Julian (1974).) (b) Contours of constant S-wave velocity in the oceanic
lithosphere and asthenosphere. The hydrous (wet) solidus and anhydrous (dry)
solidus for peridotite are approximately delineated by the 4.3- and 3.7-km s
−1
contours, respectively. The 4.3-km s
−1
contour therefore represents the boundary
between the lithosphere and asthenosphere if the base of the lithosphere is defined
as the depth at which partial melting first starts. Note the different horizontal scales
for (a) and (b). (From Duschenes and Solomon (1977).)
were extremely shallow (1-6 km) and were located beneath the median valley. The
mechanisms were nearly pure normal faulting on planes dipping at 45
◦
with strike
parallel to the local trend of the ridge axis. In addition, the focal depths decreased
with increasing spreading rate, which is consistent with the theory that the max-
imum epicentral depth is representative of the depth at which the lithosphere
ceases to deform in a brittle manner and ductile deformation takes over.
Figure 9.12 shows detailed P- and S-wave-velocity models of a mid-ocean
ridge. These models were derived from a thermal model similar to the models
discussed in Section 7.5.2 by estimating the dependence of seismic velocity
on temperature and melting for a wet (0.1% water) peridotitic mantle. The large