Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
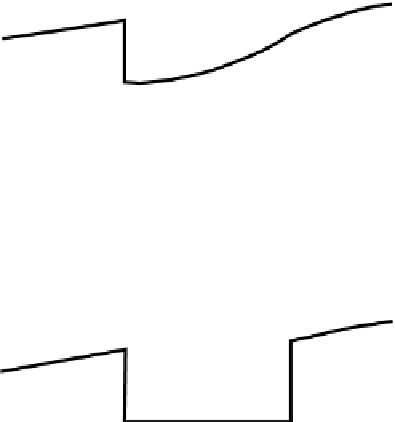
Figure 8.22.
Schematic
diagrams of possible
melting temperatures for
the mantle and core and
the actual temperature
profile. Heavy line,
melting curve; lighter line,
actual temperature
profile. (a) Chemically
homogeneous core. As
the core cools, the inner
core grows. (b) The inner
and outer core have
different chemical
compositions and hence
different melting
temperatures. An outer
core composed of an Fe-S
or Fe-O alloy would have
a much lower melting
temperature than would a
pure-iron inner core.
(a)
MANTLE
OUTER CORE
INNER CORE
(b)
MANTLE
OUTER CORE
INNER CORE
the shock-wave experiments, the samples are subjected to core pressures only
instantaneously. High-pressure and -temperature diamond-anvil and shock-wave
experiments on iron and iron compounds have produced differing results that are
difficult to reconcile. Hence there is considerable uncertainty about temperatures,
pressures and the resulting phase diagram for iron. However, present estimates
based on these experiments and on
ab initio
theoretical calculations are
∼
6000 K
for the melting temperature of pure iron and
5600 K for the melting temperature
of an iron alloy, both at the outer-core-inner-core interface. The temperature at
the centre of the Earth is 6000
∼
500 K. Figure 7.16(b) shows estimates of the
probable temperature structure within the Earth. The higher temperatures for the
mantle are similar to those shown in Fig. 7.16(a) for a two-layer mantle, while
the lower temperatures are for a single-layer mantle.
That the outer core is liquid and the inner core solid is a consequence of the
melting curve for iron. The temperature in the outer core is above the melting
temperature of iron and so the outer core is molten. The temperature in the inner
core is below the melting temperature and so the inner core is solid (Fig. 8.22).
If the core is chemically homogeneous and if it is slowly cooling, the inner core
will progressively grow with time and the inner-core-outer-core boundary will
be at the melting temperature of iron. If the inner core and outer core are of
±