Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
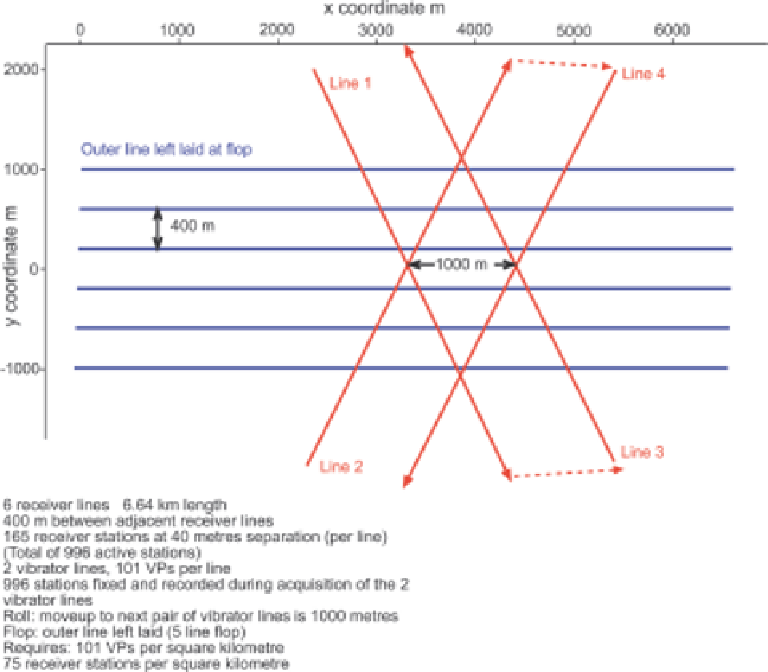
Fig. 2.17
Land acquisition. Basic X design.
Several vibrator trucks are often used together to increase the energy of the source,
and cycled several times at the same location so as to be able to sum the results of
different shots and increase the signal strength relative to noise in the records. After
shooting is completed at one shot location (often called vibrator point or VP for short),
the trucks drive to the next location. In areas of easy access and few obstacles this is a
relatively efficient process and it is possible to shoot as many as 800 VPs per day. This
is, however, still far below the efficiency achieved in marine work. Source and receiver
positions are surveyed (generally by Global Positioning System, GPS) and are marked
in advance by flags so as to allow rapid movement to the next VP. Once a section has
been shot, the cable is picked up by the field crew and added further along the line
ready for later shooting, so as to allow continuous operations during daylight hours.
Many different layouts of shots and receivers are available for land operations in areas
without obstructions, and the skill of the survey designer is to ensure the most efficient
arrangement that provides the required data quality.
Figures 2.17
-2.19
show how the