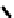Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
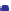
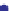
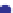
Porosity vs K
d
45
40
Murphy et al. (1993)
K
d
= 38.18 (1
−
3.39
φ +
1.95
φ
2
)
35
30
K
d
25
20
North Sea Tertiary Trend
15
10
Gulf Coast example
Troll
5
0
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
Shallow unconsolidated
example
Porosity
Fig. 5.26
Plot of observed dry bulk modulus against porosity for some real sandstone examples.
Broken black line
=
empirical lower bound for these data.
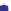
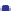
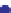
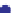
Porosity vs
m
45
40
Murphy et al. (1993)
35
2
)
µ
= 42.65 (1
−
3.48
φ +
2.19
φ
30
µ
North Sea Tertiary Trend
25
20
15
Oseberg
10
Troll
Shallow
unconsolidated
example
5
0
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
Porosity
Gulf Coast example
Fig. 5.27
Plot of observed shear modulus against porosity for some real sandstone examples.
Broken black line
=
empirical lower bound for these data.
5.6
Assessing significance
In all but the simplest cases, assessing the significance of an amplitude anomaly
(or the lack of one where it might be expected) is difficult. When investigating an