Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Position
D
e
p
t
h
E
A
B
D
C
T
o
w
a
y
i
m
e
E
A
C
B
D
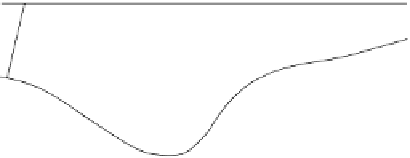
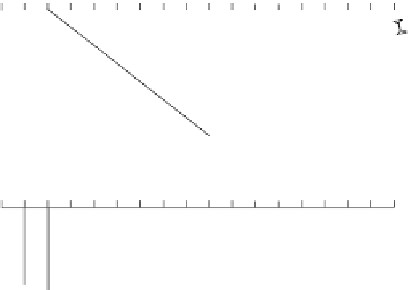
Fig. 1.1
Sketch of normal-incidence rays and resulting time section.
path of the incident ray to the reflector, so the angle of incidence at the reflecting
horizon must be 90
◦
. Not only are reflection points not directly below the surface point
wherever this horizon is dipping, but for some surface locations there may be several
different reflections from the horizon, and for other surface locations there may be no
reflections received at all. The display produced by plotting seismic traces vertically
below the surface points will, as sketched in the lower half of
fig. 1.1
, be hard to interpret
in any detailed sense. This problem is solved by a processing step called
migration
,
which repositions reflectors to their correct location in space. There are various ways
of carrying this out in practice, but the basis of one method (
Kirchhoff summation
)is
reflector is to be thought of as a 'cat'seye' that reflects any incident ray directly back
along the path by which it arrived. If a seismic line is shot above such a reflector, it
appears on the resulting section as a hyperbolic event. This suggests a migration method
as follows. To find the amplitude at a point A in the migrated section, the hyperbola
corresponding to a point scatterer at A is superimposed on the section. Wherever it
crosses a trace, the amplitude value is noted. The sum of these amplitudes gives the
amplitude at A in the migrated section. Of course, not all the amplitude values in the
summation truly relate to the scatterer at A; however, if there are enough traces, energy
received from other scatterers will tend to cancel out, whereas energy truly radiated
from A will add up in phase along the curve. (A more complete discussion shows that
various corrections must be applied before the summation, as explained, for example,