Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Locality S3
Palaeogene dolerite sill intrusives
Section 7
WDBE
TS2
TS2
TDSS
FSe
FSe
TDDP
FSd
FSd
Bar
FSc
Bar
TDDP
IHS
TDDP
IHS
(C)
(B)
Locality S3
Section 1
Section 4
Section 8
Key Surfaces
AU
AE
*
t/m
110
100
FSc
100
SU1/TS3
*(
t)
100
90
MFS1
FSb
*
t
90
MRS1
*
t
-
90
80
TS2
*
t
*
t
80
MFS1
80
70
FSa
FSe
70
*
t
70
60
8
FSd
*
t/(m)
60
4
60
50
1
*
t
*
t
Figs.
C & D
50
FSc
(D)
50
40
*
t
40
50
FSc
40
30
TDDP
?FS
?
30
40
30
20
*
m
/
t
FSb
20
20
*
t
*
m/t
10
TDDP
30
MRS1
M
M
M
10
M
10
0m
FSb
Silt
Sand
MFS1
TDDP
20
0m
Clay
Gr.
Pbl.
FSa
0m
Sand
Clay
Gr.
Pbl.
Sand
Silt
Clay
Gr.
Silt
Pbl.
TS1
10
TDDF
sandstone
siltstone
mudstone
Marine and terrestrial palynomorphs
Terrestrial and marine palynomorphs
*
m/t
Locality S3
*
t/m
*
t
Section 8
0m
Terrestrial palynomorphs
Sand
Clay
Silt
Gr.
Pbl.
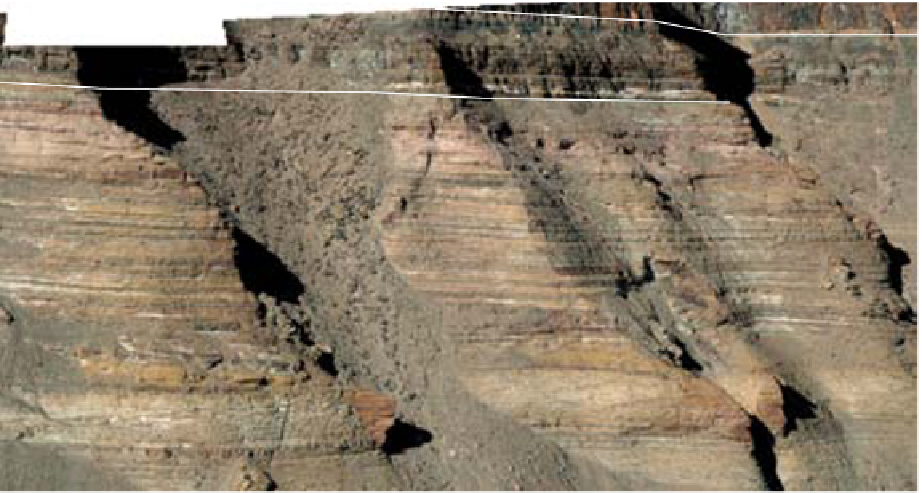
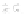
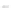
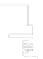
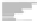
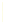
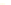
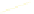
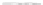
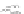
Fig. 9.
(A) The sandstone-dominated architectural elements TDDP and TDSS are composed of traceable heterolithic
upward-coarsening or upward-fining units (UCU and UFU) within the lower stratigraphical compartment. The mudstone-
dominated heterolithic architectural element WDBE overlying the TDSS element in the southern area is commonly dis-
torted by Palaeogene dolerite sill intrusives. The hummocky-stratified beds are seen as light-colored beds towards the base
of the WDBE architectural element. (B) Traceability of the flooding surfaces within allostratigraphic unit 2 vary between
































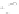







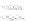











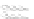
























































































































































































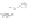












































































































































































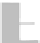































































































































































































































































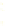

















































































































































































































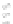













































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search