Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 6
Continued.
failure plane was formed in the backfill. For all the RW models, the major failure
pattern of the walls was overturning, which was associated with bearing capacity
failure in the ground beneath the wall toe for the cantilever-, leaning-, and
gravity-type RWs. For these conventional-type RWs, two differently inclined
failure planes (plus a vertical failure plane starting from the heel of the wall in the
case of the cantilever-type wall) developed in the unreinforced backfill.
In particular, for the leaning- and gravity-type RWs, the first failure plane
developed much earlier than the second failure plane (Fig. 6b and c). This
progressive formation of multiple failure planes can be explained by considering
the effects of strain localization in the backfill soil and associated postpeak
reduction in the shear resistance from peak to residual values along a previously
formed failure plane, as schematically shown in
Fig. 7
and described in detail by
Koseki et al. (1998b). Such behavior was not observed in the tilting tests and the
sinusoidal shaking tests, where localized shear displacements were accumulated
in the backfill only along a single failure plane. These different behaviors are due
possibly to the difference in the duration of peak load conditions. Note also that,
for the cantilever-type wall, two failure planes were formed almost
simultaneously during the irregular shaking test.
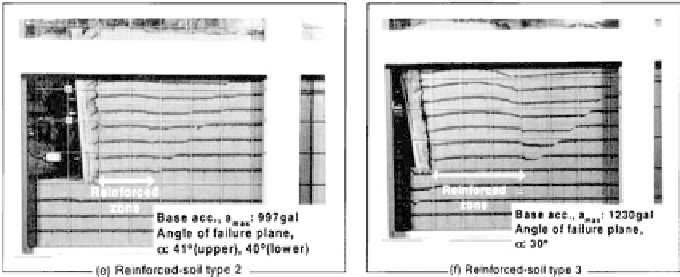
For the reinforced soil RWs, as seen from Fig. 6d-f, a two-wedge failure
mechanism, as assumed in the current seismic design practice in Japan (refer to
Fig. 8;
Horii et al., 1994, for the details), was observed. However, no failure plane
could be observed at the bottom of the front wedge in the reinforced zone (i.e.,
along segment OP in Fig. 8). This was possibly because the development of
the shear band was relatively small along this part, which could not be identified
as no dyed sand layer crossed the shear band. Importantly, the front wedge did not
behave as a rigid body, but it exhibited simple shear deformation along horizontal
planes. Similar behavior was observed in the tilting tests and the sinusoidal









Search WWH ::

Custom Search