Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
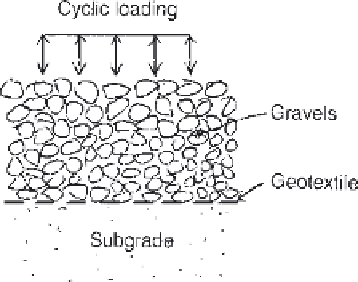
Figure 4
Geotextile as separator in unpaved roadway.
3.5 Coastal and Environmental Protection
Geotextiles are placed under erosion control structures, such as rock ripraps and
precast concrete blocks
(Fig. 5a).
They are also used as silt fences at construction
sites so that the soil particles are arrested from the runoff water.
Geotextiles are also used as geocontainers on land or underwater as storage
for slurry and for coastal protection. On land, the dredged materials or sands are
pumped under pressure into sewn geotextile sheets. The geotextile inflates to
form a tube (Fig. 5b). Geotextile tubes are extremely effective in dewatering the
high-water-content slurry/sludge by acting as a filter. The geotextile tube may
also be used as an alternative to dike and coastal protection. In such applications,
the strength and filter characteristics of the geotextile are important design
criteria.
Geocontainers are used for the disposal of potentially hazardous dredged
materials and offer a more environmental-friendly means of disposing dredged
materials offshore. The geotextile sheets are laid at the bottom of dump barges,
filled with dredged sediments, and sewn. The containers are then transported to
the disposal site and dumped via a split hull barge.
4 GEOMEMBRANES AND GEOSYNTHETIC CLAY LINERS
4.1 Geomembranes
Geomembranes are thin sheets of polymeric material that inhibit the flow of
liquid or gas. They are produced as panels and seamed at the site. Polyethylene
and polyvinyl chloride are two major polymers used to manufacture









Search WWH ::

Custom Search