Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
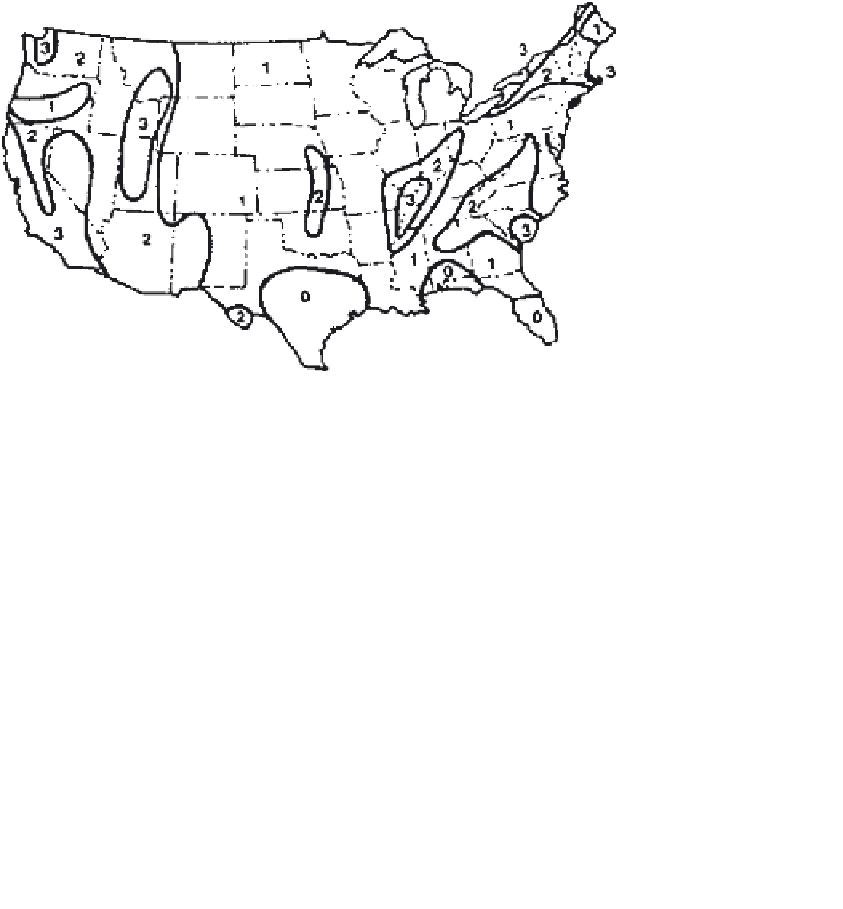
Figure 2
Seismic map. (From AASHTO, 1983.)
impractical for such high seismic loading. Note that an alternative design
methodology has also been proposed by Koseki et al. (1998) where Mononobe-
Okabe analysis is modified for retaining wall design with the failure plane
determined using the peak angle of internal friction, but the strength of the soil is
based on the residual value.
2 YIELD ACCELERATION
The concept of yield acceleration can best be illustrated by a rigid block resting
angle of friction between the block and the plane, respectively. The force
equilibrium equations are obtained for the traction T and normal force N:
T
¼
k
h
W
ð
3
Þ
N
¼ð
1
2
k
v
Þ
W
ð
4
Þ
The interface friction is governed by Coulomb's law:
T
¼
tan f
b
N
ð
5
Þ
When sliding occurs, the coefficient of horizontal acceleration equals the
yield value, which is obtained by solving Eqs. (3)-(5):
k
hy
¼ð
1
2
k
v
Þ
tan f
ð
6
Þ








Search WWH ::

Custom Search