Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
air range from 1 to 30 ppbv (Table 3.3). Table 4.3
shows that toluene is decomposed almost exclusively
by OH(g). The hydroxyl radical breaks down toluene
by abstraction and addition. The respective pathways
are
4.3.6. Ozone Production from Terpenes
The background troposphere and urban areas are
affected by biogenic emissions of isoprene and other
terpenes.
Biogenic emissions
are produced from bio-
CH
2
H
2
CO O
+ O
2
(g)
+ OH(g)
Benzylperoxy
radical
8%
H
2
O(g)
Benzyl
radical
O
CH
3
O
CH
3
H
OH
(4.53)
CH
3
Toluene-hydroxyl-
radical adduct
+ O
2
(g)
+ OH(g)
H
92%
Toluene
CH
3
OH
OH
o
-Hydroxytoluene
+ HO
2
(g)
o
-Cresol
logical sources, such as plants, trees, algae, bacteria,
and animals. Strictly speaking,
terpenes
are hydrocar-
bons that have the formula C
10
H
16
.Loosely speak-
ing, they are a class of compounds that include
hemiterpenes [C
5
H
8
(g)] such as
isoprene
;monoter-
penes [C
10
H
16
(g)] such as
The benzylperoxy radical, formed from the abstrac-
tion pathway, converts NO(g) to NO
2
(g). It also results
in the formation of
benzaldehyde
[C
6
H
5
CHO(g)],
which, like formaldehyde and acetaldehyde, decom-
poses to form ozone. The toluene-hydroxyl radi-
cal adduct, which is also a peroxy radical, converts
NO(g) to NO
2
(g). Cresol reacts with OH(g) to form
the methylphenylperoxy radical [C
6
H
5
CH
3
O
2
(g)],
which converts NO(g) to NO
2
(g), resulting in O
3
(g)
formation.
The most important organic gas producing ozone in
urban air is
xylene
[C
6
H
4
(CH
3
)
2
(g)] (Table 4.4), which
is present in gasoline, lacquers, and glues. Its mixing
ratios in polluted air range from 1 to 30 ppbv (Table 3.3).
As with toluene oxidation, xylene oxidation is primarily
through reaction with OH(g). Oxidation of xylene by
OH(g) produces peroxy radicals, which convert NO(g)
to NO
2
(g), resulting in ozone formation.
-pinene
, and
d-
limonene
;sesquiterpenes [C
15
H
24
(g)]; and diterpenes
[C
20
H
32
(g)]. Isoprene is emitted by sycamore, oak,
aspen spruce, willow, balsam, and poplar trees;
-pinene
,
-
pinene is emitted by pines, firs, cypress, spruce, and
hemlock trees;
-pinene is emitted by loblolly pine,
spruce, redwood, and California black sage trees; and
d-limonene is emitted by loblolly pine, eucalyptus, and
California black sage trees, and by lemon fruit.
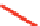
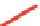
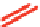
Table 4.3 shows that OH(g), O
3
(g), and NO
3
(g)
decompose isoprene. The reaction pathways of isoprene
with OH(g) produce at least six peroxy radicals. The
pathways are

























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search