Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
However, after prolonged application of ammonium sulphate, and without liming, the
soil may become acid, or 'sour'. The aluminium itself may then start to be dissolved
out of the clay lattice to form salts which are harmful to plants. This is one of the more
subtle effects of 'acid rain' whose importance we are only now coming to understand.
F
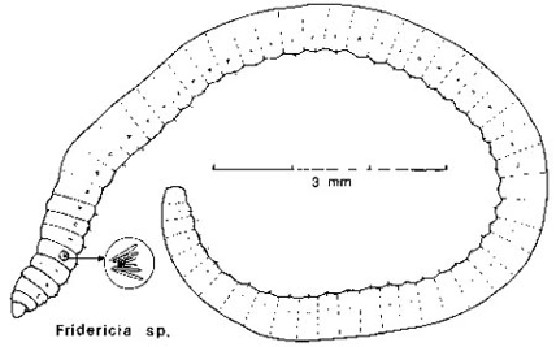
IG. 5
An enchytraeid worm from woodland soil. They are like miniature earthworms but without pigment.
Compare with
Fig. 34
. (Drawn by B.N.K.D.)
Other fertilizers, such as sodium nitrate and potassium sulphate, act through the
same processes of cation exchange, though with various minor differences. Illite clays
contain potassium in the crystal lattice itself linking the silicon and aluminium sheets;
though it is not readily exchangeable, it can act as a reservoir for potassium over a
long period.
The power of attracting and exchanging ions also explains the way in which cer-
tain pesticides, in particular the herbicides diquat and paraquat (e.g. Weedol), are ad-
sorbed and rendered inactive. Other less strongly ionized herbicides and insecticides
are not bound by clays in this way. The chlorinated hydrocarbon (= organochlorine)
insecticides (e.g. DDT) are not adsorbed by clays but bound by organic matter in a
different way.
A more familiar aspect of soil chemistry is soil acidity for this is often expressed
clearly in the vegetation. Acidity of aqueous solutions is measured by the concentra-
tion of free hydrogen ions. Pure water, H
2
O, is considered to be neutral, and has one
free H ion (and one free OH ion) to every 10 million water molecules (i.e. a concen-
tration of 10
-7
) in which the H ions are still firmly bound to the OH ions. A strong