Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
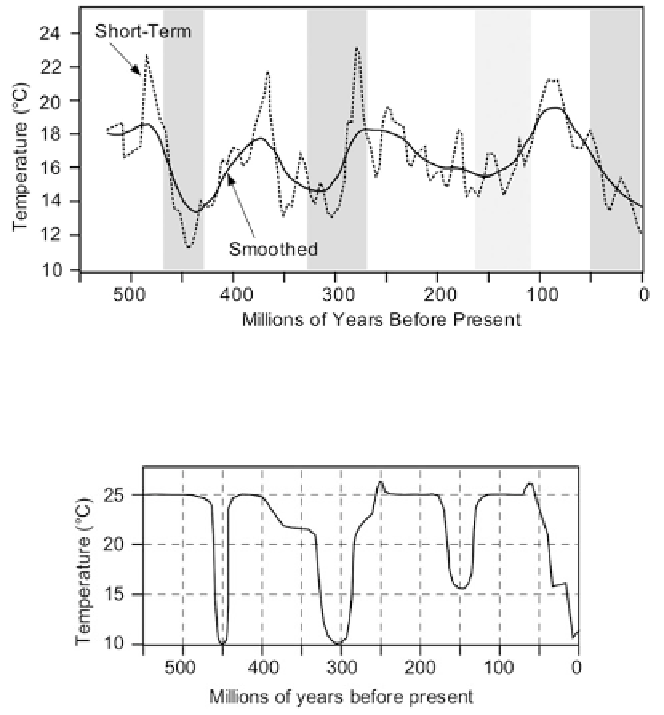
Figure 2.27. Temperatures derived from
d
18
O values of calcitic shells for the Phanerozoic
(adapted from Ziegler). Darker shading represents very cold glacial periods. Light shading
represents a cool period.
Figure 2.28. Estimate of global average temperature for the Phanerozoic (adapted from
Scotese, 2002).
See
Figure 2.27
. This figure has been used by a number of websites and
encyclopedias but it is not clear what the original source is.
There is some considerable variance between various rough estimates of the
Phanerozoic climate (see
Figure 2.28
). Nevertheless, the following salient points
seem to be generally agreed upon:
(1) For much of the Phanerozoic, global average temperatures were perhaps as high
as 25
C as compared with present day temperatures of about 14
C, showing that
for much of the Proterozoic the Earth was a veritable hothouse of warmth.
(2) There were two deep glacial cold periods embedded in the Phanerozoic, during
which evidence exists that glaciation may have reached latitudes down to 30
,
and global temperatures dropped to perhaps as low as 10
C. The ranges over
which these occurred were roughly 470-440 and 330-280 million years ago. The
Search WWH ::

Custom Search