Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
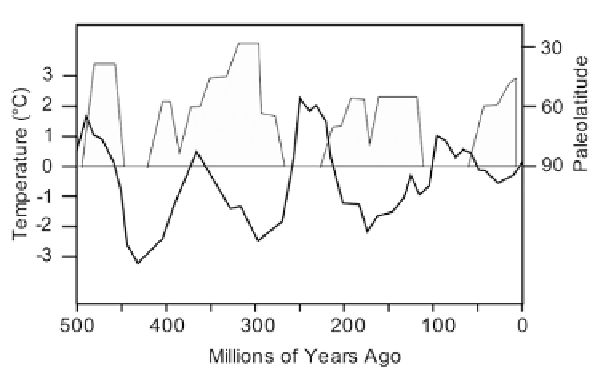
Figure 2.24. Estimated variations of tropical seawater temperatures during the Phanerozoic
(heavy line). The extent of glaciation (paleolatitude) is shown as shaded areas (adapted from
Veizer et al., 2000; Veizer, 2005).
isotope ratio, and this, in turn, reflects the ambient seawater temperature.'' In
earlier work, Veizer and co-workers ''generated a large database of several thou-
sand well-preserved calcitic shells that cover this entire 545 million years timespan.
Such detrended isotope data correlate well with the climatic history of the planet,
with tropical sea surface temperatures fluctuating by perhaps 5 to 9
C between the
apexes of icehouse and greenhouse times, respectively.''
Veizer (2005) indicated: ''the record of climate variations during the
Phanerozoic shows intervals of tens of millions of years duration characterized by
predominantly colder or predominantly warmer episodes, called icehouses and
greenhouses, respectively. Superimposed on these are higher order climate oscilla-
tions, such as the episodic waning and waxing of ice sheets.'' Veizer's estimates for
Phanerozoic climates are shown in
Figure 2.24
.
Royer et al. (2004) corrected estimates of sea surface temperature during the
Phanerozoic due to changes in pH of the oceans induced by changes in the CO
2
level of the atmosphere and changes in Ca concentrations and the calcium carbon-
ate saturation state in seawater. Their result is shown in
Figure 2.25
,
in which
paleo sea surface temperatures are greatly increased when CO
2
concentrations are
higher.
Subsequently, Shaviv and Veizer commented on the paper by Royer et al.
(2004) and Royer et al. replied to their comment. According to Shaviv and Veizer:
''The analysis of Royer et al. (2004) assumes an unrealistically high pH
correction. First, it neglects the ice-volume effect, which changes the relation
between
d
18
Oand
D
T. Second, this large pH correction implies high tempera-
tures for seawater even during times of extensive glaciations. Moreover, the
analysis of Royer et al. (2004) consists of bootstrapping, by introducing a
Search WWH ::

Custom Search