Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
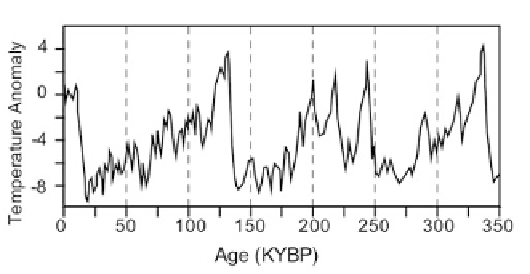
Figure 3.11. Chronology of Antarctic ice core temperatures (Kawamura, 2009).
depth, chronology is determined from the O
2
/N
2
ratio, and isotope depletion at
that depth is thereby assigned a date. While Kawamura has described this as
orbital tuning, that is misleading because it does not assume that the astronomical
theory is correct; it only assumes that the O
2
/N
2
ratio is proportional to SH
insolation. Their results are shown in
Figure 3.11
.
3.2.7 Synchronizing the dating of ice cores from Greenland and Antarctica
The timing of climatic events in the two hemispheres is of great importance in
building a better understanding of climate change. Comparison of Greenland and
Antarctic ice records can be accomplished using atmospheric gas records for
correlation. Ice cores from high accumulation rate sites are preferable as they
minimize uncertainties in the difference between the age of the gas and the age of
the surrounding ice matrix (
D
age). Atmospheric trace gases with lifetimes exceed-
ing the inter-hemispheric mixing time and showing significant changes in the past
can be considered as time markers on a global scale. The most prominent trace
gases routinely measured on extracted air from ice cores are CO
2
,CH
4
, and N
2
O.
In addition,
d
18
O has also been used as a marker. Atmospheric CH
4
and
d
18
O
have been the preferred markers because the reconstructed CO
2
concentration
suffers from in situ production in Greenland ice cores and N
2
O shows sporadic
artifacts occurring at depth intervals with elevated dust concentrations. CH
4
is of
especial interest for three reasons: (a) the past atmospheric signal is reliably
recorded in ice cores from both polar regions, (b) it shows large temporal concen-
tration variations, and (c) it closely follows Greenland rapid climatic variability
during the last glaciation and deglaciation (Blunier et al., 2007; Loulergue et al.,
2007).
3.2.8 GISP2 experience
Meese et al. (1997) described the processes used to date GISP2 ice cores. Age
dating of the GISP2 ice core was accomplished by identifying and counting
annual layers using a number of physical and chemical parameters that included
Search WWH ::

Custom Search