Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
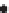
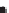
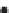
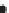
a)
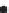
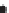
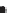
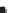
b)
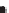
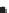
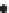
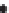
c)
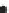
Inferred stratigraphy - layered units
Irregular pattern of widely spaced sources
Absence of sources
Many tightly clustered sources
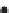
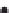
Fold
hinge
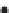
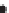
Intrusive
complex
Intrusive units
Sub-circular source patterns, moderate number of sources
Sub-circular regions with sources at their edges
Intense concentration of sources - skarn?
Intrusions
at depth
Intrusions
at depth
Linears
Faults (linear boundary between different source patterns)
Dykes (linear pattern of sources)
Figure 2.42
A cautionary note. (a) Map of source locations as might be obtained from a geophysical dataset. (b) Linear alignments identified
within the distribution, and (c) a possible geological interpretation of the data. Although apparently plausible, the source distribution is in fact
random. The figure illustrates the human propensity for seeing patterns where none exist.
sequence intruded by various igneous rocks. Depending on
the local geology, sites considered favourable for mineral-
isation might be the intersection of the major fold and the
largest fault in the survey area, or where faults are associ-
ated with the intrusive rocks. Although apparently geo-
logically plausible, there is an underlying problem: the
dataset comprises 500 randomly distributed points. There
is a high probability that any distribution of points will
show spatial alignments that form linear and curvilinear
features, and also clusters, many or even all of which have
no significance. Interpreters can easily fall into this trap
when other data
interpretation. In fact, it is very common for humans to
mistakenly
find structure in random datasets, as described
by Taleb (
2001
) in the context of the analysis of stock
markets and more generally by Shermer (
2011
).
How can traps like those described be avoided? Unfor-
tunately, there is no panacea, but the following cautionary
strategies are generally applicable and can help the inter-
preter to avoid common mistakes:
One reason that it was possible to create geological
'
from a random pattern was that only one form
of presentation of
sense
'
are not
available
to guide
the
the data was used for
the




































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































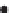






































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search