Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
T
o
d
i
st
a
nt
e
le
c
tr
o
d
e
(N
)
To distant
electrode (
Current
electrode
Potential
electrode
To distant
electrode (
A
)
N
)
V
X
B
M
B
M
T
o
d
is
ta
n
t
e
l
ec
t
ro
d
e
(
A
)
I
M
B
Z
Pole-pole
Z
=
X
BM
b)
n
.
X
MN
X
MN
Potential
electrodes
To distant
electrode (
Current
electrode
X
M
N
A
)
n
.X
M
N
V
B
M
N
N
T
o
d
i
st
a
n
t
e
le
c
tr
o
d
e
(
A
)
I
M
45°
45°
45°
Z
B
Alternative
plotting point
Pole-dipole
Z
=
X
MN
(
n
+1/2)
2
c)
X
AB
n
.
X
MN
X
MN
X
MN
Current
electrodes
Potential
electrodes
n
.
X
M
N
V
AB
M
N
X
A
B
N
M
45°
45°
I
B
Z
A
Dipole-dipole
Z
=
X
MN
(
n
+1)
2
d)
X
AB
X
MN
X
MN
X
MN
X
AB
=
3
X
M
N
Current electrodes
X
MN
X
M
N
Potential electrodes
X
M
N
I
A
M
N
B
V
B
N
M
A
Wenner
Z
Z
=
X
AB
/3=
X
MN
e)
X
AB
X
MN
X
AB
Current electrodes
Off-centre
poten
tial elec
trodes
X
MN
I
B
Potential electrodes
V
A
M
N
B
N
M
45°
45°
A
x
Schlumberger
Z
X
A
B
y
Alternative
plotting point
(off-centre potential
electrodes)
X
M
N
B
I
V
L
N
Z
=
X
AB
/2
A
x
M
Gradient
Figure 5.40
The commonly used electrode arrays and plotting conventions for soundings and pseudosections: (a) pole
-
pole, (b) pole
-
dipole,
(c) dipole
-
dipole, (d) Wenner, (e) Schlumberger and gradient arrays.




























































































































































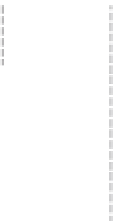
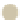














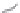












































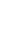
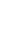

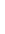























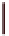

























Search WWH ::

Custom Search