Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
a)
Primary magnetic field
Current
flow
direction
(turn-off)
Coil experiences a
constant magnetic field
Current
flow
direction
Field
direction
in centre
of coil
Field
direction
in centre
of coil
(turn-off)
Switch
V
I
Transmitter
coil
Receiver
coil
Amplitude
Amplitude
+
+
On
Off
0
0
Time
Time
-
-
Current in
transmitter coil
emf in
receiver coil
b)
Coil experiences a continuously
changing magnetic field
Current
flow
direction
Current
flow
direction
Field
direction
in centre
of coil
Field
direction
in centre
of coil
I
V
Transmitter
coil
Receiver
coil
Amplitude
Amplitude
+
+
0
0
Time
Time
-
-
Current in
transmitter coil
emf in
receiver coil
c)
Current
flow
direction
(turn-off)
Current
flow
direction
Field
direction
in centre
of coil
(turn-off)
Field
direction
in centre
of coil
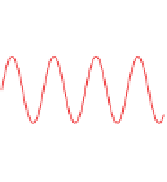
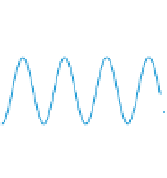
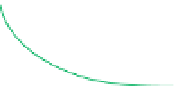
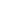
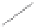
Figure 5.9
Inducing an emf in a coil using magnetic
fields created by (a) an intermittent d.c. current and
(b) a continuous a.c. current. The relationship
between the transmitter current and the receiver
voltage is shown. (c) Induction of eddy currents in a
conductor. The magnetic
Switch
I
Conductor
d)
Transmitter
coil
field of the eddy currents
approximates the primary magnetic
field. (d)
Magnetic
field of current carrying loop of wire.
























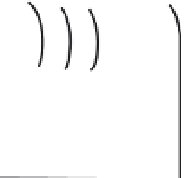






























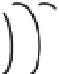































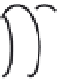


































































































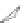








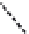

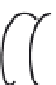





























Search WWH ::

Custom Search