Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
SB
Intrusions
Rhyolite
Qtz diorite/monzonite
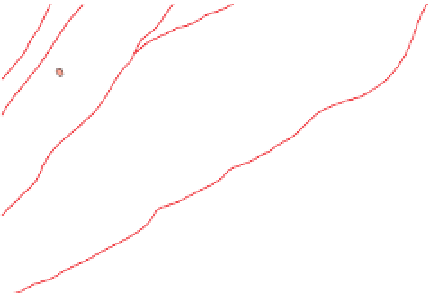
Faults
44° 24
CF
CD
PCF
GC
Major mine
Mine
Occurrence
Data points
0 2
Kilometres
LB
a)
114°45'
-3.0
-2
0
-2.5
2
6
-2.0
4
44° 24'
44° 24'
-2.0
-2.0
-2.0
4
-3.0
8
0
-2.0
-2.5
2
-3.0
6
4
-2.0
-2.5
6
2
-2.0
114°45'
114°45'
b)
c)
-0.5
-1.5
2.6
2.7
44° 24'
44° 24'
0.0
-0.5
2.6
2.6
2.7
2.7
2.6
-0.5
2.5
-1.5
-1.
5
-1.0
-0.5
0.0
0.0
2.5
0.0
-0.5
2.6
d)
114°45'
e)
114°45'
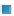
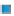
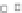
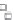
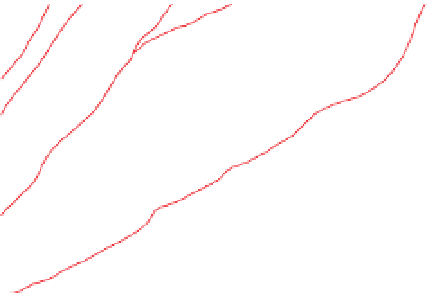
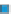
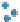
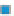
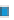
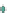
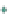
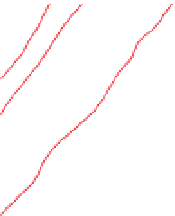
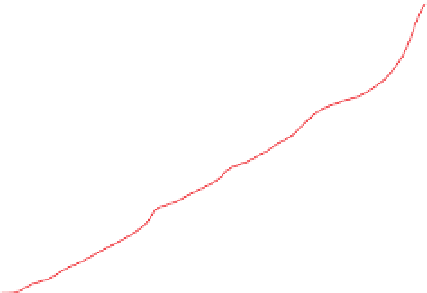
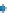
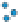
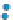
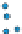
Figure 3.57
The hydrothermal alteration system associated with the Yankee Fork mining district. (a) Simpli
ed geology and occurrences of
mineralisation. CD
-
Charles Dickens Mine, CF
-
Custer Fault, GC
-
General Custer Mine, LB
-
Luck Boy Mine, PCF
-
Preacher
'
s Cove Fault.
18
O analyses. (c) Contours of the logarithm of magnetic susceptibility
(SI). (d) Contours of the logarithm of strength of remanent magnetism (A/m). (e) Contours of density (g/cm
3
). The hydrothermal alteration
has produced a general decrease in magnetism and variable density. Note the increase in density near the Charles Dickens Mine and decrease
around the General Custer and Lucky Boy mines. Based on diagrams, or created using data, from Criss et al.(
1985
).
(b) Contours of hydrothermal alteration as indicated by whole-rock
δ
argillic and intense propylitic alteration tends to destroy
magnetite, although less intense propylitic alteration may
allow magnetite to survive. In contrast, the potassic alter-
ation zone is magnetite rich, especial in Au-rich systems
(Hoschke,
2011
).
alising hydrothermal system in the Yankee Fork mining
district, Idaho, USA. The system contains Ag
-
Au vein
mineralisation (
Fig. 3.57
), which occurs within Eocene
calc-alkaline lavas, tuffs and intrusives, and the area is






























































































































































































































































































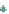



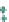


















































































































































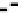

Search WWH ::

Custom Search