Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
C
s
s
s
sand
clay
organic
(-)
(-)
(-)
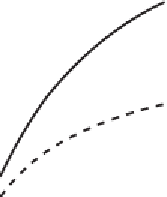
Figure 2.22
Sketch of the dependence of soil thermal properties on soil moisture for
three soil types (sandy soil, clay soil, peat): volumetric heat capacity (left), thermal
conductivity (middle), and thermal diffusivity (right). (Based on the model of De
Vries,
1963
)
This effect is most pronounced for dry soils: the addition of a little water increases
the thermal conductivity considerably. When the water content is increased further
a stage will come where the extra water will not have a large effect: the fact that the
conductivity of water is much lower than that of the soil material causes that little
extra pathway is added with the addition of extra water.
Various empirical models for the soil moisture dependence of the thermal conduc-
tivity exist (see Farouki,
1986
, for a review). Peters-Lidard et al. (
1998
) show that
in a land-surface model (such as those discussed in
Section 9.2
) errors in the esti-
mated soil thermal conductivity not only affect the soil heat lux but also impact on
the partitioning of energy between sensible and latent heat lux. In
Section 9.1.7
one
example of a model for the thermal conductivity as a function of soil composition is
discussed.
To see the effect of water content on the diffusivity
κ
s
we have to take both the
conductivity and the volumetric heat capacity into account. Because the increase
of
λ
s
with water content levels off, whereas the increase of
C
s
with soil moisture
is linear, the diffusivity (recall that
κ
s
= λ
s
/C
s
) irst increases with soil moisture,
but at higher soil moisture contents it decreases again. This effect is sketched in
Figure 2.22
.
Question 2.19:
Given a soil with a porosity of 40%, where the matrix (60%) consists
of 20% quartz, 50% clay and 30% organic material. The pores are illed with 75% water
and 25% air (i.e., soil water content is 30%).
a) Which of
ρ
s
,
c
s
,
C
s
,
λ
s
or
κ
s
can be calculated?
b) If possible calculate the thermal soil properties (using
Table 2.2
).















Search WWH ::

Custom Search