Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
λ
1
λ
2
-
∆λ
=
D
a
W
angular
dispersion
D
a
=
W = slit width
-
λ
= (
λ
1
+
λ
2
)/2
λ
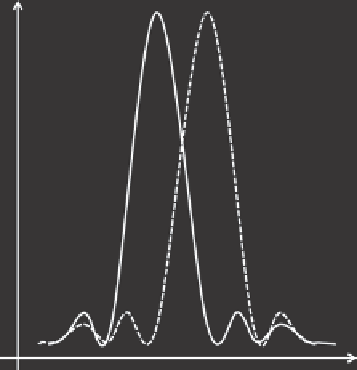
Figure 5.13. Rayleigh criterion for the resolution of two peaks.
diffraction minimum of the other (see
Figure 5.13
). Thus, the spectral resolution can
be defined by:
λ
∆
λ
=
(5.9)
DW
a
where
λ
is the average wavelength between the two lines and
D
a
is the angular dispersion
of the system, and
W
is the slit width.
Stray light can be defined as any radiation passed by the monochromator that is out-
•
side the selected spectral position and bandpass. In many cases, the specification of
stray light is made by reference to the relative amount of radiation being passed at a
spectral position defined as an integer number of bandpass values from the test source -
often a laser line. For example, a typical measurement involves filling the grating of a
monochromator. Then, an intensity measurement is made both at the wavelength of the
laser and at another wavelength eight bandpasses away from the laser wavelength. The
ratio of the latter to the former is considered the stray light of the system under this
criterion.
However, this type of approach is not realistic to the normal use of monochromators
as broad-band tunable light sources or broad-band detection system. Typically, stray light
is very difficult to measure, as it strongly depends on the wavelength, bandpass used, and
the type of source. A further discussion of this important point is made in
Section 5.4.8
on
instrument performance validation.
•
The optical throughput of a monochromator depends on the source, the slit height,
the collected solid angle, the transmission factor of the optics, and the convolution of