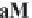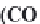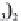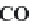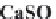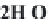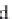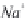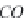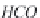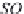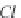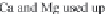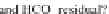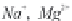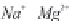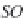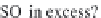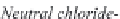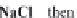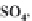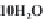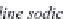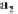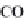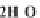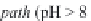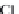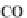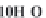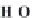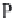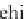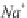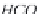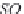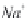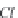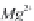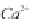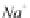Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
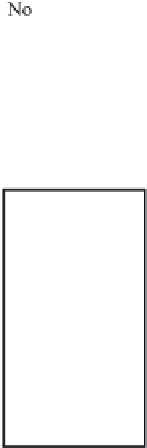
Fig. 13.11
Schematic
pathways of crystallization of salts from a saline solution [Cheverry
1974; Servant 1975; Gueddari 1984; Loyer 1991 (combined)].
fundamental characteristics of these saline environments. When
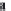
bicarbonate ions
HCO
3
-
(and also
CO
3
2
-
generally present in much
lower quantity, but in any case there is an equilibrium between
the two) are totally consumed from the start of development
through precipitation of
CaCO
3
and
MgCa
(
CO
3
)
2
, there remain in
the solution anions and cations of strong acids and strong bases.
The pH stays around 7.2-7.4. This is called the
neutral pathway
.
On the contrary, if the carbonates and bicarbonates are in excess
in the solution, as they correspond to salts of weak acids and
strong bases, the pH will rise to 9 or more. We can write