Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Between 950 and 1100 m
, the profile is differentiated. Entic Podzols
appear, characterized by two B horizons. The first, just below the
surface humus, is a Bh horizon characterized by chocolate-brown
colour and massive but not hard structure. The second, below
the first, is called Bs. Its colour is quite close to that of an orange
peel. The vegetation is fir (
Abies pectinata
) with or without under-
growth of grasses (
Deschampsia flexuosa
) or blueberry (
Vaccinium
myrtillis
).
Above 1100 m
, to the summits around 1450 m, we find typical
Podzols. These present a depleted E horizon that is continuous,
and light grey or totally white. It is sandwiched between the
black humus and the Bh, which is also dark. The vegetation is
fir forest with dense undergrowth of blueberry.
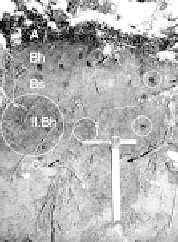
Fig. 11.1
Soil sequence on the Pilat massif. Top row: left, Cambisol Dystric; middle, soil
characterized by appearance of a yellowish-brown Bs; right, Entic Podzol (with orange Bs
and appearance of a black continuous Bh, extended by mottles—see circles); above the A
horizon the snow marks the soil surface. Bottom photograph: Podzol (appearance of an E
horizon, bleached and depleted).
Photos
: author.