Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
The net variable charge, positive or negative, will be the greater the
farther the system goes from the pH
0
. But many factors are involved,
in particular the concentration of the solution.
Oxides and hydroxides have a high PZNC (pH 7-9). The effective
pH of Andosols being much lower, these materials develop,
in situ
, an
anion exchange capacity. For clay minerals it is the reverse: their PZNC
is low (pH < 2). Therefore they exchange mostly cations at the usual
pH of soils. But we have seen that they are hardly abundant in typical
Andosols. Allophanes rich in Si have a PZNC near pH 5 so that more
cations or more anions are exchanged in different cases. Silica-poor
allophanes and imogolites have PZNC higher than pH 6. These materials
are mostly anion exchangers. Overall, Andosols form an exception in
soil science. They retain anions well, whereas other soils let them flow
into the groundwater. See, for example, the case of nitrates.
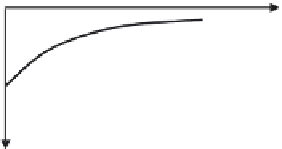
Cation exchange
capacity
CEC
Curve
symmetrical
to that of
anion
exchange
capacity
Curve obtained
by moving the
one above
pH-independent fixed
charges
Variable negative charge
(cation retention)
pH
0
pH
Anion exchange capacity
Point at which the net
variable charge is zero
AEC
PZNC =
P
oint of
Z
ero
N
et
C
harge
Fig. 10.10
Variation in cation exchange capacity (CEC) and anion exchange capacity
(AEC) with pH (Wada 1985; Radcliffe and Gillman 1985). At pH below the PZNC, the anion
exchange capacity is greater than the cation exchange capacity.
The cation exchange capacity, CEC, at the pH of the soil is low at least
in Andosols with confirmed acid nature. It is less than 2 cmol (+) kg
-1
.
But, measured at pH 7 by the standard ammonium acetate method, it
is artificially augmented because the variable negative charges increase
with pH. On the other hand, the adsorbed bases are correctly determined.
Thus an artificially low base saturation percentage is obtained. Also,
the correlations show that this CEC is related to the content of organic
Exchange capacity and adsorption complex