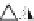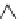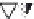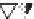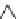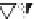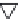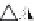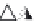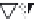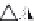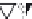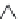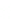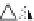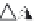Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Al
2
Si
2
O
5
(
OH
)
4
.
n
(
H
2
O
). Its basal spacing is 10 Å, which drops to 7 Å on
dehydration. The chemical formula is thus the same as that of kaolinite.
The specific surface area of halloysite is generally 30-50 m
2
g
-1
, but may
at times go up to 110 m
2
g
-1
. Its CEC, theoretically zero, can actually
reach 60 cmol (+) kg
-1
. It is presumed that this is due to the presence of
2/1 clay minerals in admixture or in the form of randomly interstratified
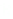
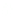
layers. Figure 10.5 shows how the interstratification occurs (Quantin
et al
.
1984, 1988; Delvaux 1988). There would be ¾ halloysite for ¼ 2/1 clay
mineral with much tetrahedral substitution.
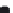
Silica tetrahedra
Octahedral sheet
Potassium
Water molecule
Layer of 1/1 type but hydrated (halloysite)
Layer of 2/1 type (smectite)
Fig. 10.5
Diagram of halloysite-smectite interstratifi cation (Delvaux 1988). Localized ab-
sence of silica tetrahedra (1/1 layer) brings about an approach of the layers and the basal
spacing diminishes.
Note
: this deformation is not shown in the diagram.
In reality, halloysite occurs as vaguely spherical or ellipsoidal
particles, as more or less hexagonal crystals, in folded lamellae, in
tubes or in spindles… These variations are related to disorders in the
octahedral sheet where iron may replace aluminium until it represents
17 per cent by weight of the mineral. There is also substitution of
magnesium for aluminium. In the tetrahedral sheet, deficiency in Si
will be favourable for appearance of a tubular structure. Increase in Si,
on the contrary, will result in formation of lamellae. This is logical but
still controversial. Halloysite is a mineral of intermediate non-perhumid
(pedo)climate. On desiccation it seems to transform to kaolinite while
retaining its Si/Al ratio of 1. As a consequence of loss of water molecules,
the basal spacing falls to 7 Å.
Metahalloysite
, a sort of dehydrated halloysite, is a mineral with
slight interstratification, intermediate between halloysite and disordered
kaolinite. Its basal spacing is 7.4 Å.
Ferrihydrite was discovered in 1970. It is known to be a hydrated
oxyhydroxide of iron. Scientists have proposed various formulae so
that nothing is as yet certain. In soils, it is something like 5Fe
2
O
3
.9H
2
O.
Ferrihydrite