Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Enderby Abyssal Plain is bounded to the north by the Southwest
Indian Ridge.
Further to the east, beyond the Kerguelen Plateau, extends the Australian
-
-
Antarctic
-
Basin which is limited in the north by the Southeast Indian and the Indian
Antarctic
Ridges. East of the Macquarie Ridge, the Ross and Amundsen Abyssal Plains and
the Bellingshausen Plain lead into the Drake Passage, limited to the north by the
Paci
c
-
Antarctic Ridge and the Eltanin Fracture Zone. The ridges have a signi
cant
in
uence on the location of major currents and fronts.
The Southern Ocean formed about 120million years ago during the Gondwana
breakup when the South American, the African and the part of the Indo-Australian
plates started to move north away from the Antarctic plate. The Paci
cplate
separated from the Antarctic plate about 100million years ago and the Australian
part of the Indo-Australian plate about 60million years ago. After the Tasmania
-
Antarctic Passage had opened about 34 million years ago and the Drake Passage about
31million years ago a circumpolar deep water
first time and changed
dramatically the climate and the biology of the whole of the southern hemisphere.
As a direct consequence of the formation of these circumpolar wind and current
systems, Antarctica cooled and the continent-wide ice sheet began to grow.
flow existed for the
Winds and weather
The Southern Ocean is a very windy place. Winds are generated by horizontal
air pressure differences which are caused by temperature and humidity gradients
between the polar and the subtropical latitudes. To the north of the Southern Ocean
(
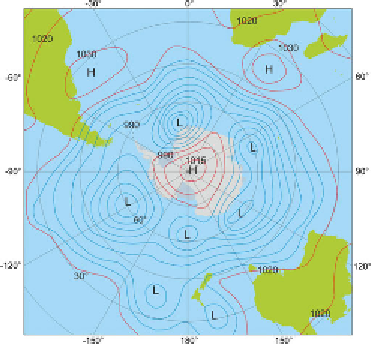
Figure 5.2
) is the subtropical high pressure belt, southward from which the air pressure
at the sea surface decreases to the low pressure trough which is centred at about 60
S. The
pressure difference between the subtropical highs and the low pressure belt, together with
the action of the rotating Earth, give rise to a band of
strong west winds, the West Wind Drift. The low
pressure belt consists of a series of moving cyclonic
systems which are continuously forming and
decaying. South of the low pressure belt, pressure
increases again towards the continent which results
in easterly winds in the Antarctic coastal areas.
Thus the West Wind Drift drives the eastward
flowing ocean current, the Antarctic Circumpolar
Figure 5.2
Atmospheric pressure distribution at sea
level displaying the major high and low pressure
systems, which determine the winds over the Southern
Ocean. (Credit: Eberhard Fahrbach, AWI)



Search WWH ::

Custom Search