Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
1.0
1.0
0.8
0.8
0.6
0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.2
0.0
0.0
0
200
400
600
a
s
800
1000
1200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
a
s
c
d
1.0
1.0
0.8
0.8
0.6
0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.2
0.0
0.0
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
a
s
a
s
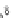
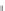
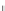
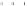
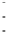
Fig. 3.2
Scatter plots of (
a
) 20,000 samples from an MCMC chain with a well tuned proposal,
(
b
)-(
d
) 1,000 samples from three test MCMC chains. In (
b
), the proposal variance is too small,
and the chain is started far from the posterior mode. In (
c
), the proposal variance is too small,
but the chain is started near the posterior mode. In (
d
), the chain is started at a point far from
the posterior mode, and with proposal variance that is initially too small. However, the proposal
variance is allowed to vary according to the characteristics of the sample during the first 1,000
iterations
outside of the mean, but the proposal variance is adaptively tuned according to (
3.9
).
The transition probability is a zero-mean multivariate Normal distribution with
standard deviation equal to 0.5 % of the commonly observed range of parameter
values. The proposal width is intentionally set too small to illustrate the potential
problems encountered when a poor start point is chosen. Because the proposal
width is small, nearly all proposed transitions are accepted (the Hastings ratio
(
3.5
) is everywhere close to 1). It thus takes some time for the chain with initially
poor start position (Fig.
3.2
b) to enter a region with reasonable probability density.





























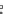


































































































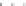
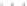


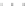







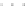




























































































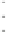























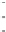





















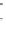













































Search WWH ::

Custom Search