Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Black Sea
Turkey
China
Tajikistan
A
B
C
D
E
Mediterranean Sea
Iran
Iraq
Afghan
Egypt
F
Saudi Arabia
G
H
I
India
Arabian
Sea
Sudan
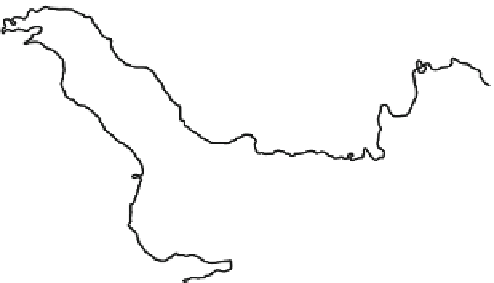
Fig. 25.1
Domain of model and subregion definition. Shaded indicates the elevation of terrain
(unit: m). The sub-regions are defined as north Iraq (
34
ı
-
36
ı
N
;41
ı
-
43
ı
E); northwest Iran
A
;
34
ı
-
36
ı
N
;46
ı
-
48
ı
E); north central Iran (
34
ı
-
36
ı
N
;54
ı
-
56
ı
E); central Afghanistan
(
B
;
C
;
34
ı
-
36
ı
N
;66
ı
-
68
ı
E); west Himalaya Mountain (
34
ı
-
36
ı
N
;74
ı
-
76
ı
E);westSaudi
(
D
;
E
;
22
ı
-
24
ı
N
;41
ı
-
43
ı
E); east Saudi Arabia (
22
ı
-
24
ı
N
;51
ı
-
53
ı
E); Arabian Sea
Arabia (
F
;
G
;
22
ı
-
24
ı
N
;63
ı
-
65
ı
E) and Northwest India (
22
ı
-
24
ı
N
;70
ı
-
72
ı
E)
(
H
;
I
;
Observed temperature.
The maximum and minimum temperature at the 2-m level
with
0:5
ı
0:5
ı
gridded datasets are created by the NOAA's CPC, which is taken
from observational stations of the WMO GTS datasets. The interpolation method is
based on the previous rainfall estimation algorithm (
Xie et al. 1996
).
Analyzed temperature and wind field.
The temperature and wind fields are taken
from the NCEP Global Forecasting System (GFS) analysis data (GFS ANL), which
is gridded to a horizontal resolution of
1
ı
1
ı
.
25.4
Topography and Evaluation Method
To investigate the spatial heterogeneity of complex terrain in SWA region, nine
representative sub-regions are depicted in Fig.
25.1
. They are defined as north
Iraq (A;
34
ı
-
36
ı
N,
41
ı
-
43
ı
E); northwest Iran (B;
34
ı
-
36
ı
N,
46
ı
-
48
ı
E); north
34
ı
-
36
ı
N,
54
ı
-
56
ı
E);
34
ı
-
36
ı
N,
central Iran
(C;
central
Afghanistan (D;
66
ı
-
68
ı
E); west Himalaya mountains (E;
34
ı
-
36
ı
N,
74
ı
-
76
ı
E); west Saudi
22
ı
-
24
ı
N,
41
ı
-
43
ı
E); east Saudi Arabia (G;
22
ı
-
24
ı
N,
51
ı
-
53
ı
E);
Arabia (F;
22
ı
-
24
ı
N,
63
ı
-
65
ı
E); and west India (I;
22
ı
-
24
ı
N,
70
ı
-
72
ı
E).
Arabian Sea (H;



























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search