Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
c
d
e
f
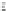
Fig. 24.13
The Longwang (2005) (
a
,
c
,
e
) and Sinlaku (2008) (
b
,
d
,
f
) cases. Temperature (
shaded
;
K) and wind (
vector
;ms
1
) components of the evolved Ran Err from (
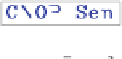
a
and
b
) CNOP Sen, (
c
and
d
)CSV Sen, and (
e
and
f
)Ran Area on the level 0.7 at the final forecast time. The
boxes
(
dashed
)
indicate the verification areas; the
boxes
(
solid
)for(
e
)and(
f
) indicate the Ran Areas (From
Chen
and Mu 2012
)
Table 24.2
TC Longwang (2005) and TC Sinlaku (2008). The statistical averages of the final
verification dry energy norms of evolved Ran Errs from CNOP Sen, CSV Sen, FSV Sen and
Ran Area (J kg
1
), respectively (From Chen and Mu, Table 2)
Dry Energy (Verification Area)
CNOP Sen
CSV Sen
FSV Sen
Ran Area
Mean (40) (TC Longwang)
22.24
14.03
0.33
0.24
Mean (40) (TC Sinlaku)
27.03
19.28
19.28
7.35
the previous experiments. The geographical distribution of the 40 local areas,
including CNOP Sen, CSV Sen, FSV Sen,and37RanAreas, is shown in Fig.
24.14
. Notably, the locations of these areas are defined around the initial storm
center to the far outside, and the distance between the centers of two adjacent areas
is defined as two-grid spacing for TC Sinlaku (2008) and as one-grid spacing for
TC Longwang (2005). Table
24.3
shows the results of the extended experiments
for both cases. Every unit of the tables (except units in the first row and column)
corresponds approximately to its location in the geographical distribution of the
40 areas as shown in Fig.
24.14
. For TC Longwang (2005), the statistical value






























































































































































































































































































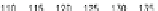






































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































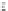
















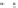









































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search