Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
c
CNOP
CNOP
CNOP
37N
12h
37N
24h
37N
36h
31N
10
8
6
4
2
31N
10
8
6
4
2
31N
10
8
6
4
2
25N
25N
25N
19N
19N
19N
13N
13N
13N
111E
120E
129E
138E
111E
120E
129E
138E
111E
120E
129E
138E
Fig. 24.7
TC Meari (2004). The vertically integrated energies of CNOP (
shaded
, units: J/kg) for
the first approach. (
a
) for 12 h forecast, (
b
) for 24 h forecast, and (
c
) for 36 h forecast (From
Zhou
and Mu 2012b
)
a
b
c
CNOP
CNOP
CNOP
12h
24h
36h
39N
39N
39N
10
8
6
4
2
10
8
6
4
2
10
8
6
4
2
33N
33N
33N
27N
27N
27N
21N
21N
21N
15N
15N
15N
111E
120E 129E
138E
111E
120E 129E
138E
111E
120E 129E
138E
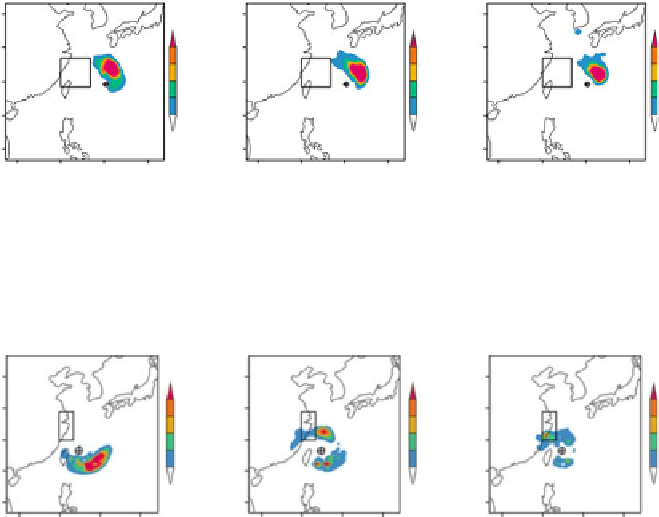
Fig. 24.8
Same as Fig.
24.7
, but for TC Matsa (2005) (From
Zhou and Mu 2012b
)
For the second approach, the sensitive areas of the linear case move to the
verification areas as the initial time is shifted closer to the forecast time (i.e., as
the optimisation period is shortened; Fig.
24.9
). This result is consistent with the
results of previous studies that applied linear methods to cases that permitted linear
approximation (
Palmer et al. 1998
;
Kim et al. 2004
;
Wu et al. 2007
). In such
case, the background field such as the subtropical high plays an important part
in the corresponding targeted forecasts. In the nonlinear case, the sensitive areas
fall in disrupted-ring patterns around the initial typhoon centres, and are mainly
located inside the typhoon circulation (Fig.
24.10
). This indicates that the targeted
forecasts in this case are affected primarily by conditions within the typhoon,
while the background fields play a relatively smaller role. The results of these two
cases suggest that the deployment of targeted observations intended to improve the
forecast at a special time may depend strongly on the time of deployment. The time
at which the targeted observations are deployed is thus of crucial importance.
Generally, the results of this study have shown that the deployment of targeted
observations to improve a special forecast depends strongly on the time of deploy-
ment and it should be adaptive to achieve large improvements for different targeted
forecasts.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search