Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
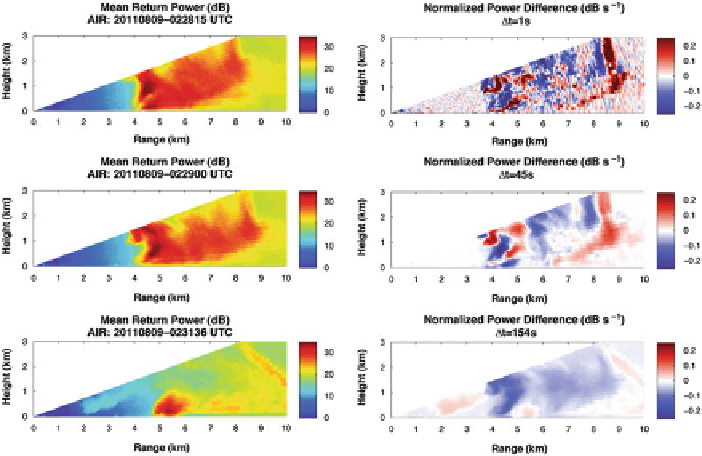
Fig. 18.18 Selection of temporal discretization of Z for entropy anomaly
. Range corrected
power calculated from the Atmospheric Imaging Radar (AIR) are shown in the
left column
at 0228:15, 0229:00 and 0231:36 UTC. The
right column
shows the calculated DZ values for
temporal intervals of 1, 45 and 154 s. Note the dipole structure has degraded in the 154-s interval
indicating advection dominates the microphysical phase changes within the radar resolution
volume. A temporal resolution of less than 1 min is necessary to reduce the advection bias and
obtain measurements appropriate for entropy estimation
since the dipole structure visible in the 1-s interval is still intact, the microphysical
information required for the entropy derivation is still present and accurate.
From this experiment, it is determined that high temporal resolution is necessary
for meaningful and accurate measurements of DZ, and thus entropy. Revisit times
(
t) of 1 min or less would be appropriate for reflectivity or power measurements
and would ensure that environmental advection does not significantly bias the
estimates for entropic balance theory.
18.13
Providing a Basis for Tornado Data Assimilation
The entropic balance theory was described and its theoretical applicability for
tornadogenesis was shown in the Sects.
18.2
,
18.3
,
18.4
,
18.5
,
18.6
,
18.7
,
18.8
,
18.9
,and
18.10
. Some key questions of tornado and environment (Appendix 1)
are answered well by the entropic balance theory (Appendices 2 and 3). All
of the governing equations of atmospheric dynamics, thermodynamics and mass
continuity for the flow of high Reynolds number can be derived from the Lagrangian
Search WWH ::

Custom Search