Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
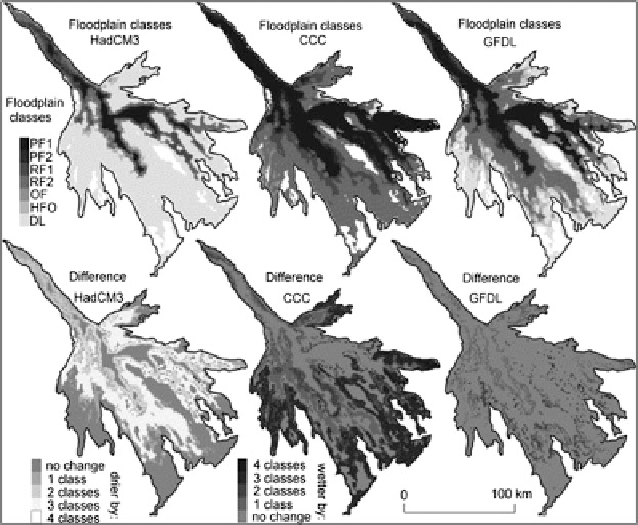
Fig. 17.3
Effects of change in hydrological inputs on the Okavango Delta as obtained from various
climate models (HadCM3, CCC and GFDL) under A2 greenhouse gases scenario for 2020-2050
period (Adopted from
Murray-Hudson et al.
(
2006
))
The IPCC reports that during recent years several studies have focused on diverse
applications of RCMs for impact studies which include downscaling from the
climate model scale to the catchment scale, using regional climate models to create
scenarios to drive hydrological models and quantifying the effect of hydrological
model uncertainty on estimated impacts of climate change (
IPCC 2007b
).
17.1.3
Dynamically Downscaled Climate Model Input
for Hydrological Studies
Although the GCMs provide reasonable simulation accuracy of climate in a global,
hemispheric or a continental scale, at a regional/sub-regional scale representa-
tion, the simulation accuracies are poor due to their coarse spatial resolution
(
Giorgi 1990
,
1996a
,b).
Regional climate is often affected by forcings and circulations that occur at a
sub-grid scale of the GCM. Some of the regional and local scale climate forcings
due to land-use characteristics, complex topography, land-ocean contrasts, aerosols,
radiatively active gases, snow, sea ice and ocean currents are not resolved well by
Search WWH ::

Custom Search