Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
25
20
15
10
Total energy consumed
Fossil fuel consumed
Fossil fuel produced
5
0
1980
1985
1990
1995
2000
2005
2010
Year
(b)
Electricity
generation, 10%
Agriculture: nitrous
oxide, 15%
Transport, 19%
Agriculture:
methane, 32%
Other energy, 16%
Waste, 2%
Industrial and
solvents, 6%
Fig. 8.9
(a)NewZealand'sfossilcarbondomesticproduction,consumptionandoverall(includingnon-fossil)energy
forthepastthreedecades.(b)NewZealand'sgreenhousegasemissionsbysectorin2008(Ministryforthe
Environment,2011).
the opposition parties say that they will campaign on removing these measures should
they win the general election, which is at present scheduled for 2013.
New Zealand, of all this topic's case study nations, is the one least dependent on
fossil fuel (see Figure 8.9). New Zealand is not a big greenhouse emitter either as a
nation or on a national per-capita basis. Nearly 40% of its energy comes from HEP
and renewable energy sources, and it is proportionally least dependent on fossil fuel
of all the nations discussed above. This is in no small part because historically it has
relied heavily on fossil fuel imports, proportionally more so than any other nation
examined in this chapter, although in gross terms its imports have been smaller.



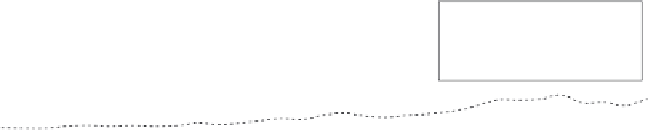


























Search WWH ::

Custom Search