Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
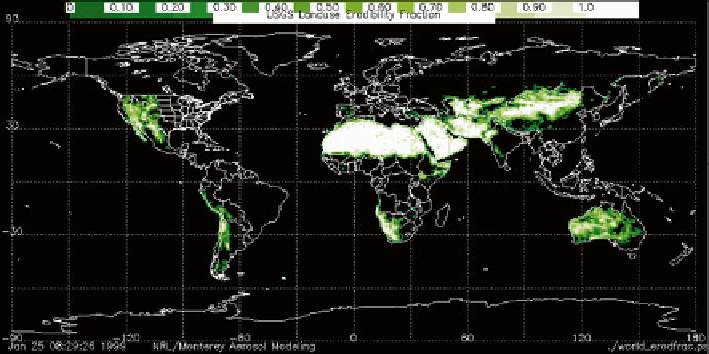
Fig. 8.3
Global dust-producing regions based on land-use erodibility fraction identifi ed by the
United States Geological Survey (NRL
2009
)
8.3
Geographic and Climatic Implications
8.3.1
Transboundary Dust Travel
Dust storms not only impact their origin area, but also can impact land, water and
people a great distance away where dust, and the particles it carries, fi nally settles.
For example, dust particles originating in inner and southern Mongolia and northern
China contribute to dust events in Japan, the Democratic People's Republic of
Korea, the Republic of Korea and the Taiwan Province of China, causing seasonal
'yellow sands' and muddy rains (Lee and Liu
2004
; Kimura
2012a
,
b
). In the south-
ern hemisphere, dust storms originating in eastern Australian can carry dust parti-
cles across the Tasman Sea to New Zealand, signifi cantly contributing to soil
development and geochemical cycles (Marx et al.
2009
). As a result, creating poli-
cies pertaining to dust storm mitigation (i.e. vegetation restoration efforts) or devel-
oping early warning communication can be challenging. Further, since climatic
changes will not affect all regions of the world in the same way or to the same
degree, its infl uences on dust storms and their travel patterns is relatively unknown,
thereby projecting uncertainty on populations that experience dust storms.
One of the most pronounced transboundary sources of dust is the Sahara Desert.
Dust originating in the Sahara is frequently carried extended distances - east across
the Nile Delta region and Mediterranean Sea, west across the Atlantic Ocean to the
Caribbean, the USA, parts of Central and South America and north over to Europe.
Dust originating in the Sahara has been reported as reaching as far east as Turkey in
April 2012 (Mühr et al.
2013
). This dust transport can negatively affect air quality,
causing health and visibility problems (Prasad et al.
2010
), but can also positively
contribute to rainforests in Central and South America (Sivakumar
2005
).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search