Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
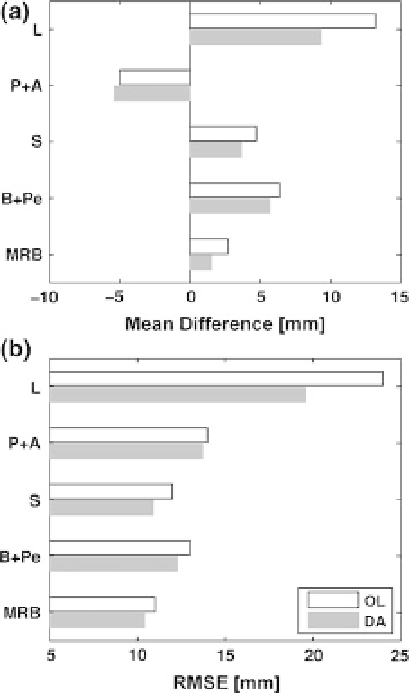
Fig. 4 SWE statistics of a mean
difference and b RMSE for open
loop (OL; white) and assimilation
(DA; light gray) of GRACE
TWS retrievals relative to CMC
SWE estimates via Sturm et al.
(
2010
). Statistics are for the
Mackenzie River Basin (MRB)
and its sub-basins Liard (L),
Peace and Athabasca (P ? A),
Slave (S), and Bear and Peel
(B ? Pe) shown in Fig.
3
.
Adapted from Forman et al.
(
2012
)
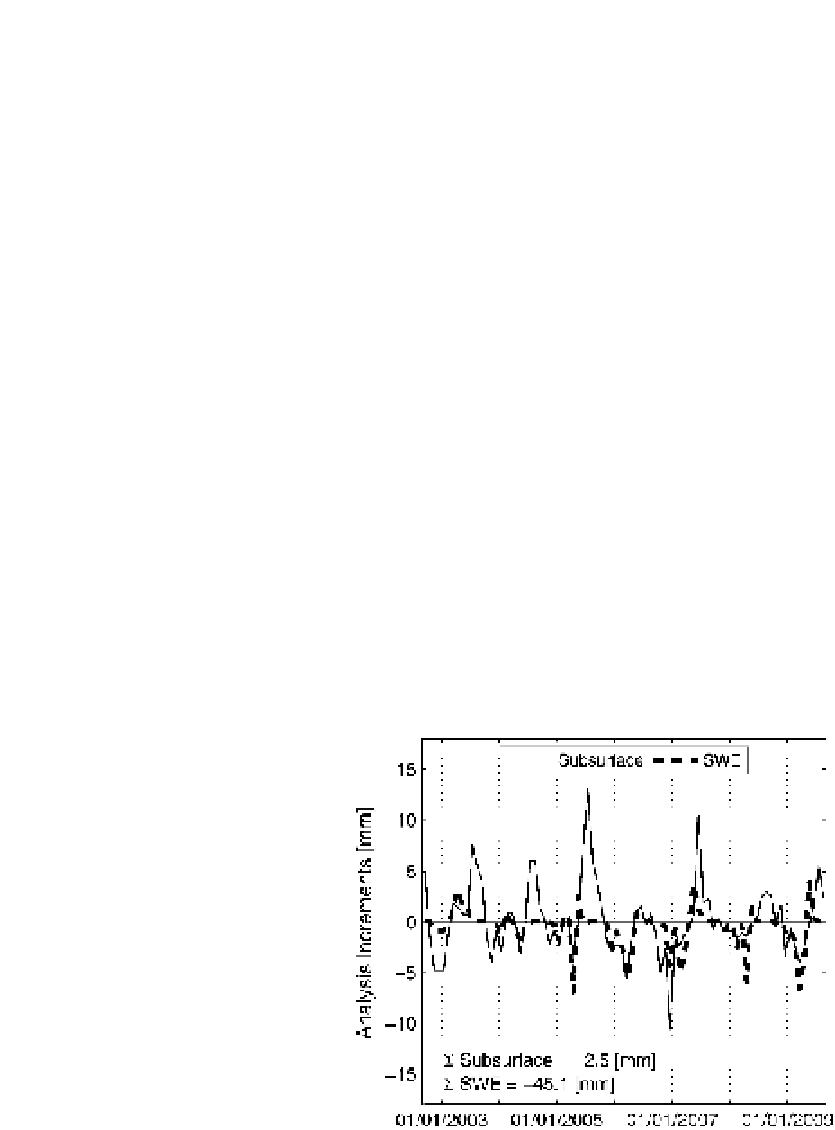
Fig. 5 Analysis increments for
the entire Mackenzie River basin
from GRACE TWS assimilation.
The thin, solid line represents the
subsurface water increments,
whereas the thick, dashed line
represents the SWE increments.
Adapted from Forman et al.
(
2012
)
The results shown in Figs.
4
and
5
imply that the assimilation procedure can effectively
partition the vertically integrated GRACE TWS retrievals into their snow and subsurface
water components. Houborg et al. (
2012
), Li et al. (
2012
), Su et al. (
2010
), and Zaitchik
et al. (
2008
) further investigated the horizontal, vertical, and temporal disaggregation of
GRACE TWS retrievals and reached similar conclusions for other basins in North America
and Europe in different climate zones. Collectively, the growing body of research suggests