Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
End
Start
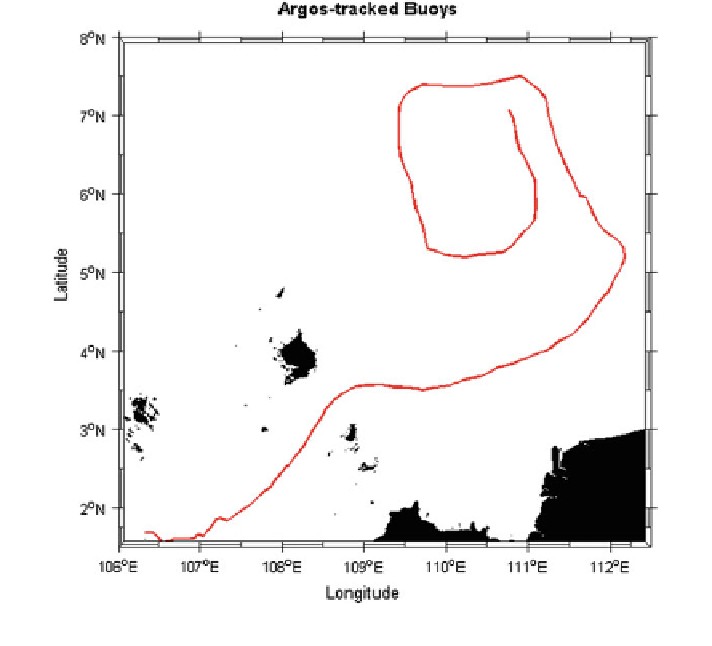
Fig. 3
Track of drifter 49596 (red line) from 1st December 2005 to 2nd January 2006
4.3 Analysis of Seasonal Surface Circulation
In order to understand the seasonal changes in surface circulation, geostrophic
currents are computed from the long term averaged SLA (1993-2011) and plotted
based on the monsoon season. The analysis is focused at four specific months
April, August, October, and December. April and October represent the monsoon
transition periods, while August and December represent the NE and SW mon-
soon, respectively. April is the transition period from the NE to SW monsoon
system for the study region. General surface circulation in the central region of
SSCS during April is cyclonic (Fig.
5
a) and is consistent with Wyrtki (
1961
).
Originating from Vietnam coastal area, the surface current flowing southward and
part of the current turns eastward at around 3-6N, reaches Natuna Island and west
of Borneo Island as shown in Fig.
5
a. Meanwhile, the northward flowing surface
current from the Sarawak Coast branches into two at around 5N. One branch
flows northward and then turns eastward. The other branch turns north eastward
and flows along the northwest coast of Boneo Island. A cyclonic eddy has found at
around 6N, 113E and the prevalence of eddies in the region is also reported by