Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
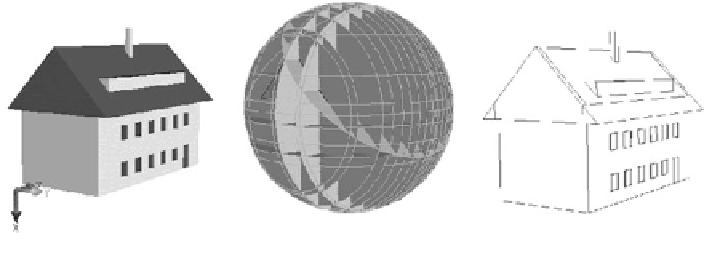
Fig. 2
Segmentation of a sample building with 34 split-planes (Thiemann and Sester
2004
)
3 Segmenting 3D City Model Objects Based on Geometric-
Semantic Decomposition
3.1 3D Segmentation Overview
Segmentation is basically a method to partition or break down an object into
simpler parts for various objectives (object detection, analysis and management,
texture mapping, etc.). Currently, 3D segmentation is heavily utilized in computer
vision and medical technology. However, the development in 3D GIS has triggered
the needs to use the tool for geospatial-related applications (You et al.
2003
;Hu
et al.
2004
; Thiemann and Sester,
2004
). Generally, there are two principal types of
segmentation; surface-type and part-type (Agathos et al.
2007
; and Shamir,
2008
).
The surface-type segmentation uses various primitives such as planes, cylinder and
sphere as an approximation of the mesh to create distinct surface regions. On the
other hand, the part-type segmentation creates volumetric parts by partitioning the
mesh into meaningful or semantic components. Figure
3
shows the result for the
part-type and surface-type segmentations.
3.1.1 Region Growing Segmentation
There are several different segmentation techniques introduced in different fields,
but based on the survey made by Shamir (
2008
), the simplest segmentation
technique is called the Region Growing Segmentation meanwhile a comparative
study on segmentation techniques done by Attene et al. (
2006
) and several other
research (Attene et al.
2006
; You et al.
2003
; Hu et al.
2004
; Manferdini and
Remondino
2010
) shows that a suitable segmentation algorithm for manmade
objects is segmentation based on primitives fitting or 3D volumetric approaches.
Region growing is also known as a local-greedy approach where it starts with a
seed element, then, examines its neighbouring elements and grows a sub-mesh
incrementally by determining whether the adjacent elements should be added to