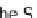Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
(b)
(a)
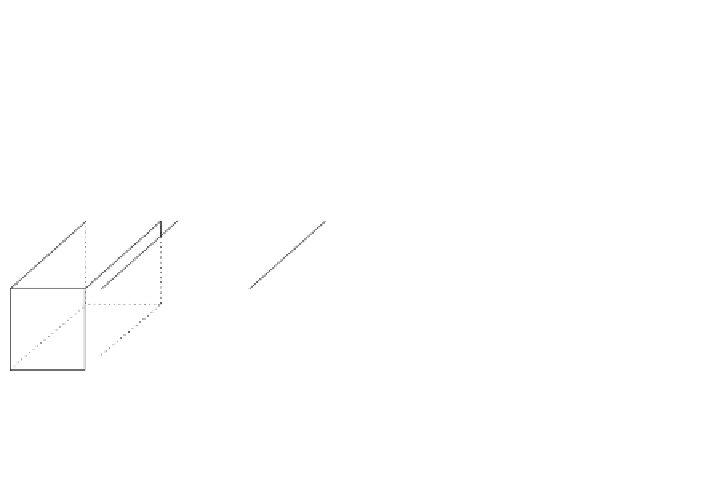
Fig. 5 The dual half-edge data structure in 3D. a The DHE models 3D subdivisions by
representing the boundary of each polyhedron separately with a graph (edges are black lines), and
two adjacent polyhedra are linked together by the dual graph (edges are dashed lines). b The
DHE pointer based data structure; the primal graph (solid lines) is connected permanently with
the dual graph (dashed lines); he-original Half- Edge; S, N
V
, N
F
, D, V - pointers.
These five pointers are necessary to represent complex models including non-
manifold cases (when more than two cells are linked by a shared lower-dimen-
sional cell. However, the number of pointers can be reduced by one if only cells
linked by a shared face are taken into consideration. Additionally, a primal and
dual Half-Edge pair can be merged and stored as a single record, since they are
permanently connected (the number of pointers is reduced by one).
Using the data structure directly, without higher level construction operators
would be extremely difficult ('manual' updating of pointers while edges are added
to a model can easily cause many mistakes). Therefore, it is preferred to use the
construction operators from Boguslawski (
2011
). They allow for model construc-
tion in an easy way, edge-by-edge, like in various CAD systems. Additionally, the
dual graph is created automatically as the edges are added to the model and single
cells are linked into a complex. These operators, used for modifications of the
existing model, make only local changes in the primal and dual graph, and thus the
whole dual graph does not need to be reconstructed after each modification.
During the construction process, the external cell, which encloses cells in a
complex representing a modelled object, is automatically created. It can be
considered as 'the rest of the world'. This external cell prevents topological
inconsistencies at the boundary of the complex, where cells do not have an
adjacent cell to connect to. Also, navigation can be implemented without testing if
a boundary of the complex is approached.
Figure
6
shows one possible way to construct two cubes linked into one
complex. It is based on CAD-like operators—Euler operators (Baumgart
1975
,