Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Hinge point
(a)
(b)
(f )
Hinge point
Inflection
point
Inflection
point
Hinge point
Hinge point
(c)
Hinge zone
(d)
limb
+
(e)
Closure
Hinge
point
Hinge
point
Inflection
point
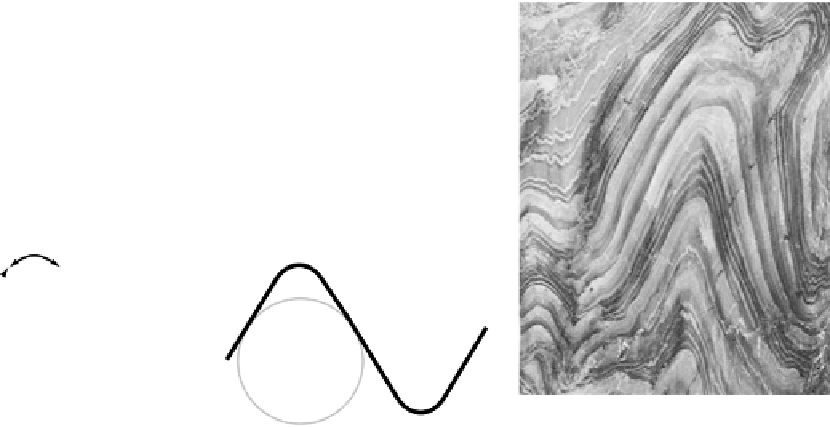
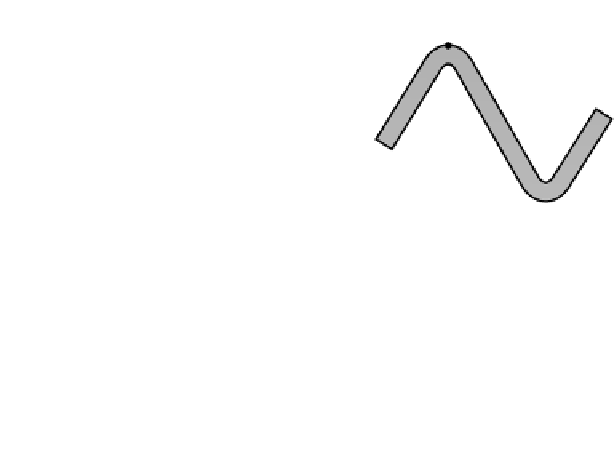
Fig. 4.115
Definition of fold geometry in two dimensions at a given transversal section of a folded surface. (a) The hinge point is the point of
maximum curvature and the inflection point of minimum curvature. (b) Semicircular folds have constant curvatures and the hinge is defined in
the middle point of the arch and inflection points where there is a change in the bend polarity. (c) A general case where there is a hinge zone,
defined on the fold segment with a higher curvature than the reference point as shown in (d). (e) Folds with two hinge points and closure.
(f) An example of folded surfaces showing different geometric elements in 2D.
can be also related to bending of a cover of ductile rocks
over some rigid basement that is fractured or to the drag
effect of shear movements along a fault.
reference circle tangent to the inflection points at both
sides of the fold. Tracing perpendicular lines from the
inflection points will mark the center of the circle
(Figs 4.114-4.115d). The
hinge point
is defined in a 2D
transverse section as the location in a folded surface show-
ing the maximum curvature. In an individual section folds
can have one or several hinge points (multiple hinged
folds). The point of minimum curvature between two
adjacent hinge points of the same fold is called
closure
(Fig. 4.115e). In three dimensions, joining all hinge points
along the surface defines the
hinge line
or
hinge
(Fig. 4.116). Low curvature areas between the hinge lines
are the fold
limbs
or
flanks
. The inflection lines can be
defined in three dimensions joining all inflection points
4.16.1
Geometric description of folds
Folds can be described by their geometric characteristic,
both in two or three dimensions. The most basic geomet-
ric elements are described in a single folded surface in two
dimensions. Additional descriptions involve the 3D exten-
sion of the folded surface, and also the relation between
several superimposed folded layers. Curvature of a fold
may remain constant or can change. It can be defined by a
















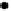












Search WWH ::

Custom Search