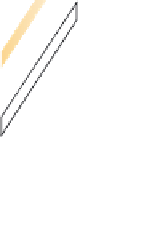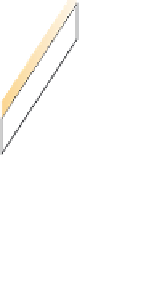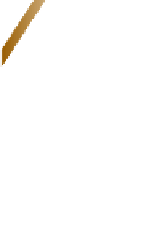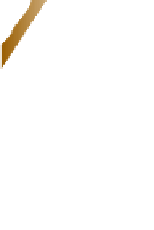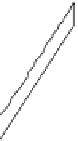Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Horizontal
motion
Horizontal
motion
Fault scarp
Vertical
motion
Vertical
motion
Upthrown
block
Downthrown
block
Upthrown
block
Downthrown
block
(a) Normal fault
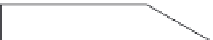
(b) Reverse fault
Horizontal
motion
Horizontal
motion
Vertical
motion at
shallower
angle
Downthrown
block
Upthrown
block
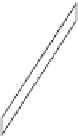
(c) Strike-slip fault
(d) Overthrust fault
Figure 13.21 Types of faults.
(a) Normal faults and (b) reverse faults result when one block
moves up while the other moves down. (c) Strike-slip faults result when blocks move horizontally
relative to one another. (d) Overthrust faults occur when the upthrown block also slides over the
downthrown block.
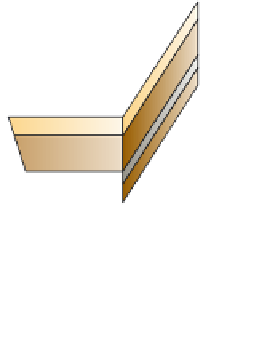
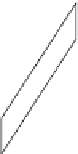
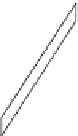
Figure 13.22 A normal fault.
This roadcut exposure
shows a small normal fault in surface rocks near Death
Valley, California. The fault plane is clearly visible as the di-
agonal contact between the two blocks of rock.