Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Anticlinal
ridge
Synclinal
valley
Anticlinal
ridge
Synclinal
valley
Anticlinal
ridge
Synclinal
valley
A
B
(a) Initial folding during Allegheny Orogeny
Hogback
ridge
Hogback
ridge
Synclinal
ridge
Anticlinal
valley
Anticlinal
valley
Anticlinal
ridge
Synclinal
valley
Synclinal
valley
Hogback
ridge
A
B
(b) After erosion of softer rock layers
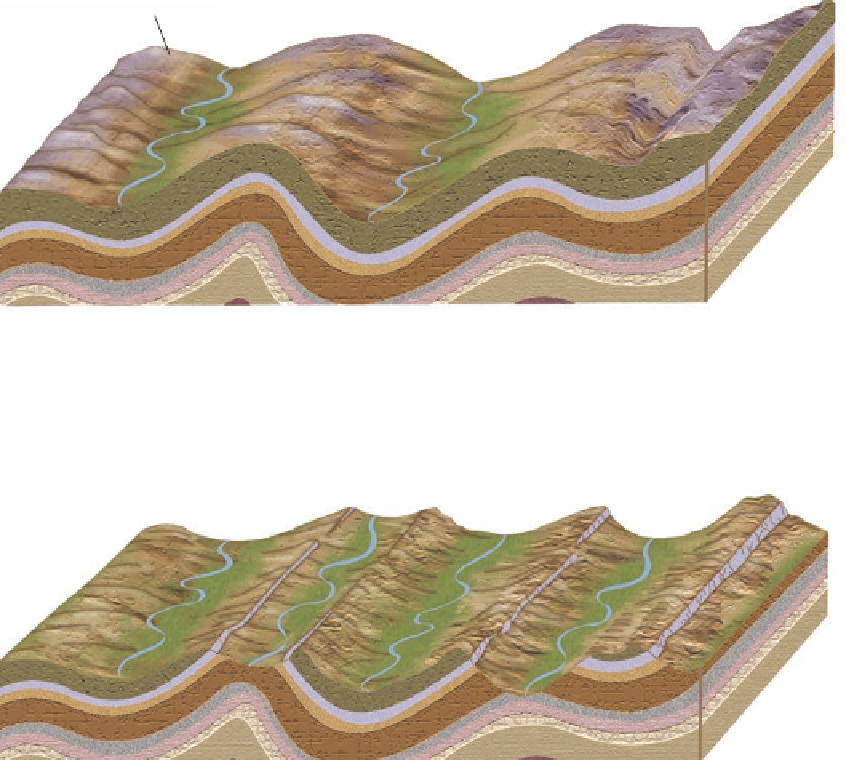
Figure 13.14 General evolution of the Ridge and Valley Province.
(a) The landscape shortly after folding. Anticlines form the high
ground, whereas valleys occur in synclines. (b) As time progresses, erosion modifies the landscape. Anticlines at
A
and
B
are eroded by
streams, forming valleys in upward-arching structures. Hogback ridges exist on both sides of the anticlinal valley at
A
, where limbs of the
former anticline form the high ground. To the right at point
B
, extensive erosion has inverted the topography so that the ridge is underlain
by a syncline.
others (such as limestone). As a result of this preferential ero-
sion, some parts of the Appalachian landscape were eroded
extensively, whereas others were not. In addition, stream ero-
sion focused on the highest points, which were the crests of
the original anticlines.
Because of this variability, the relationship between
surface topography and underlying structure in the Appala-
chians became less clear over time. Look at the ridge marked
A
in Figure 13.14b, for example. This ridge was initially un-
derlain by an anticline (Figure 13.14a). Erosion removed the
crest of the ridge, however, forming a valley parallel to the
underlying structure. The ridges on each side of the valley are
remnants of the limbs of the anticline. Such a ridge is called
a
hogback ridge
because one side of the ridge is steeper
than the other. Also note that the valley formed between the
two hogbacks at point
A
. In Figure 13.14b the ridge is under-
lain by the original anticline; that is, the rocks arch up there
as you would expect. In other words, the stream eroded into
the core of the anticline, forming a valley within it along
its length. Such a landform is called an
anticlinal valley
.
Hogback ridge
A ridge underlain by gently tipped rock strata
with a long, gradual slope on one side and a relatively steep
scarp or cliff on the other.
Anticlinal valley
A topographic valley that occurs along the
axis of a structural anticline.